Development of CO2 emission reduction technology using hydrogen in blast furnace steelmaking
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Outline
· Currently, a national project to mitigate CO2 emissions from steelworks, which is called COURSE50 (CO2 Ultimate Reduction System for Cool Earth 50), has being conducted by five private companies including four blast furnace manufacturers and one engineering company. One of the major development technologies of COURSE50 is hydrogen utilization technology for iron ore reduction in blast furnaces using hydrogen-based gas such as coke oven gas generated in steelworks.
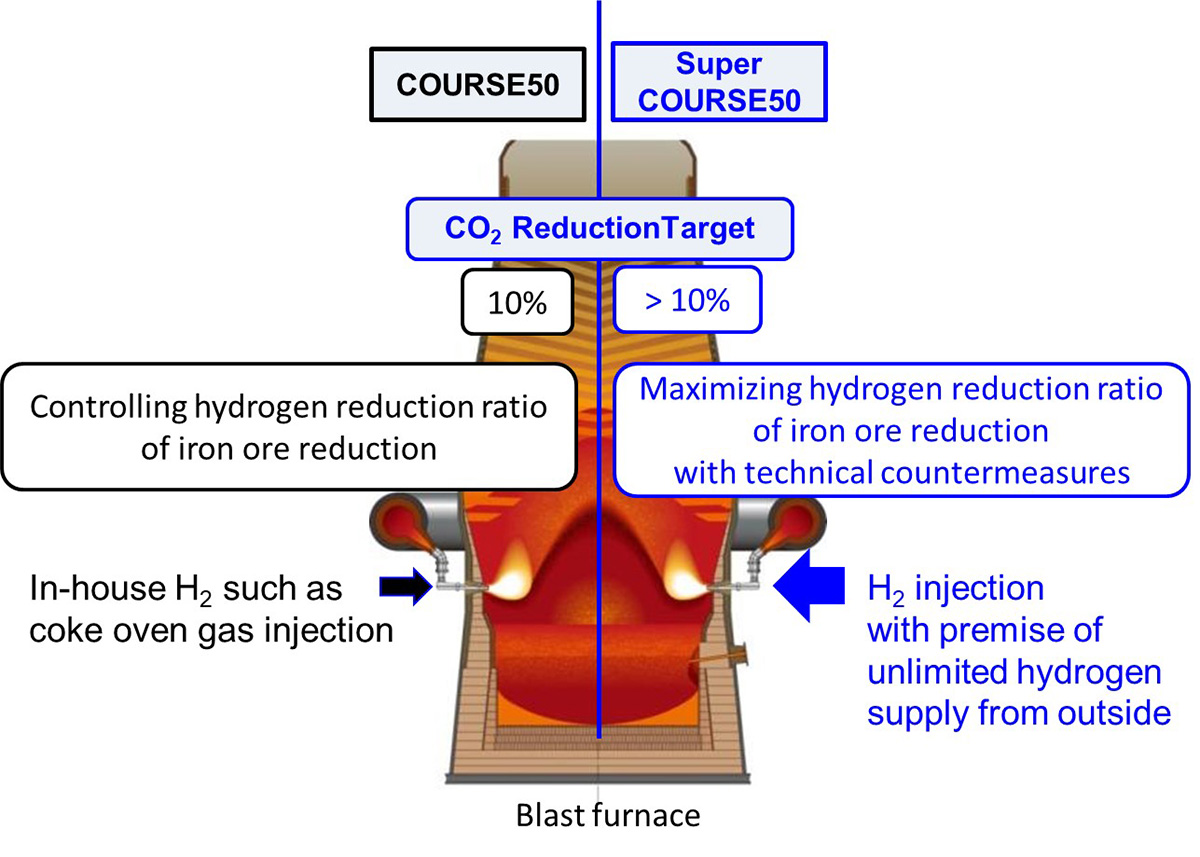
· This technology can mitigate CO2 emissions from blast furnaces by 10% by replacing a part of carbon reduction with hydrogen reduction in blast furnaces. COURSE50 utilizes in-house hydrogen source to replace a part of carbon in blast furnace. On the other hand, Super COURSE50 project aims to significantly reduce CO2 emissions from blast furnaces by more than 10% by maximizing the hydrogen reduction ratio of iron ore reduction in blast furnaces with premise of unlimited hydrogen supply from outside of steel works.
Description
a) Achievement goal in challenge
We will significantly reduce CO2 emission intensity of the blast furnace method and, in combination with CO2 separation and capture technology, establish a technology that can significantly reduce CO2 emissions by more than 30% compared to the current blast furnace method.
b) Challenges to be overcome to realize the challenge
· In particular, about 70% of the CO2 emitted by the steel industry is generated in the process of pig iron production using a blast furnace (reduction reaction that removes oxygen from iron ore, which is iron oxide, to iron). The efficiency of the use of reducing agents has improved to near thermodynamic theoretical values. Therefore, further reduction of CO2 is very difficult. In order to reduce CO2 emissions from steelworks, five companies, including four blast furnace manufacturers and one engineering company, started the national project called COURSE50 in 2008 and they are working on the development.
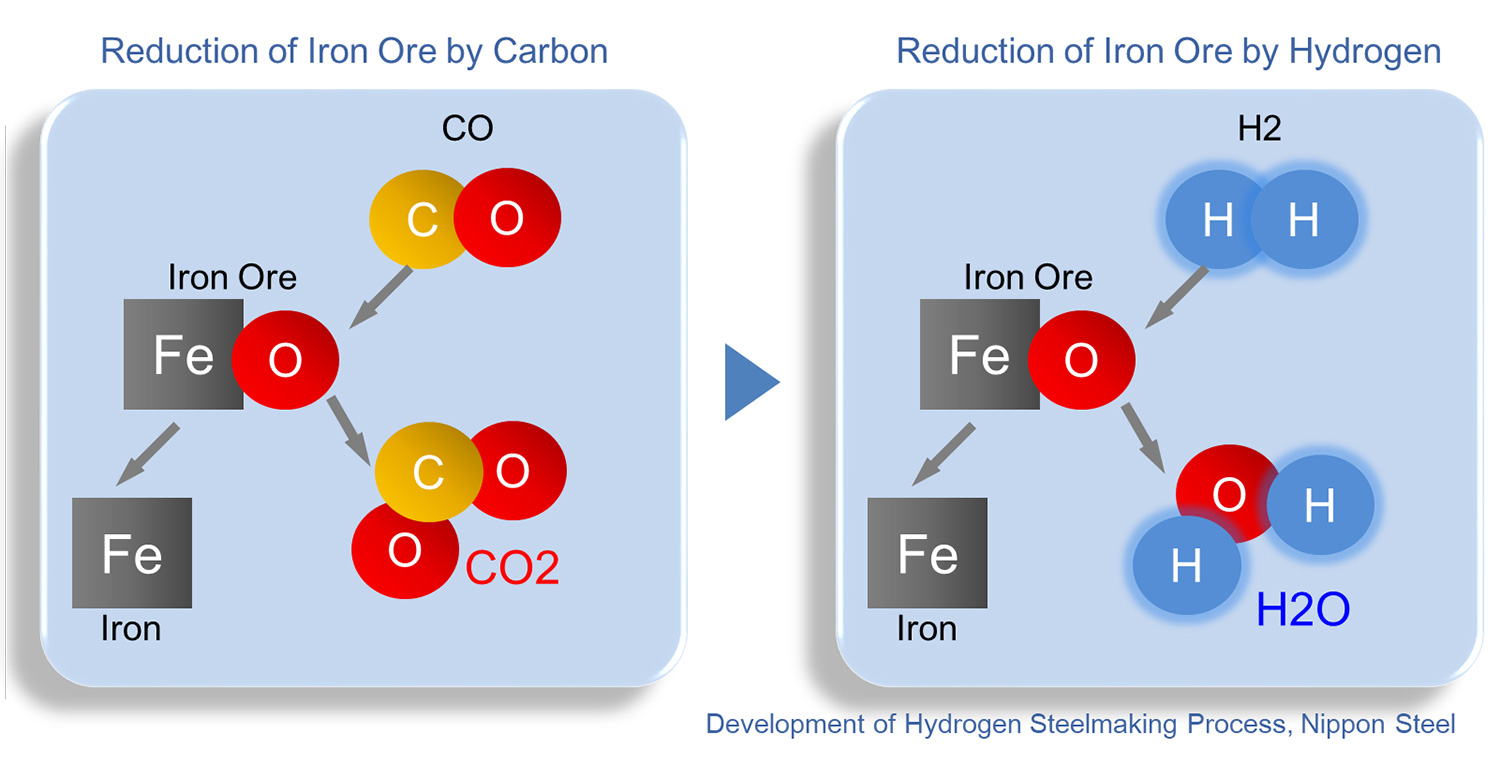
· One of the major development technologies of COURSE50 is the use of hydrogen-based gas (coke oven gas) generated in the steel works to reduce part of the reduction by carbon in the blast furnace (reaction process of removing oxygen from iron oxide to iron). This is a hydrogen-based reduction technology that reduces CO2 emissions from blast furnaces by 10% instead of reduction by hydrogen. For the time being, the blast furnace method is considered to be the mainstream of the pig iron production method, both technically and economically. Therefore, as a transition technology until the establishment of 100% hydrogen reduction steelmaking, we need to establish further low carbon technology based on blast furnace process.
c) Nippon Steel’s strengths and specific actions
· In COURSE50, we developed both theoretically and experimentally using a 3D mathematical model of our own blast furnace and a test blast furnace with a furnace volume of 12m3 (about 1 / 500th the scale of an actual blast furnace) constructed at our Kimitsu Works. We achieved our goal of reducing CO2 emissions from blast furnaces by 10%. The concept of COURSE50 was to increase the ratio of iron ore reduction by hydrogen by blowing coke oven gas (COG) containing about 60% H2 from the blast furnace tuyere. There is a limit to the amount of gas (coke oven gas). As a next step, assuming that a large amount of hydrogen can be supplied, a large amount of hydrogen-based gas outside the steelworks is used to dramatically increase the reduction by hydrogen and emit 10% of CO2 from the blast furnace at the COURSE50 target of 10%. Challenge technologies that greatly exceed reduction targets.
· The realization of this technology requires various developments to utilize the introduced hydrogen more efficiently for iron ore reduction. For example, since the hydrogen reduction reaction of iron ore is an endothermic reaction, heat compensation technology for promoting reduction of iron ore in a blast furnace is an important development subject. In addition, in terms of elemental technology that utilizes hydrogen, it is necessary to develop elemental technologies common to 100% hydrogen reduction steelmaking, such as establishing technology to stably supply a large amount of hydrogen-based gas to a blast furnace in consideration of the combustion characteristics of hydrogen.
d) Quantitative effects of realizing the challenge
· Mass supply of steel materials is our mission from the perspective of the SDGs. Dramatically reduce the CO2 emissions per unit of the blast furnace method, which is extremely excellent in terms of technology and economy, and by combining with the CO2 separation and capture technology, it is possible to significantly reduce CO2 emissions by more than 30% compared to the current blast furnace method Challenge to complete the development of the technology by around 2030.
Partner(s)
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), JFE Steel Corporation, Kobe Steel, Ltd., NIPPON STEEL ENGINEERING CO., LTD., Nippon Steel Nisshin Co., Ltd.
Supplementary information
https://www.jisf.or.jp/news/topics/181119.html
https://www.jisf.or.jp/business/ondanka/zerocarbonsteel/
Other Innovation Challenges
CO2 uptake and carbon storage as blue carbon by utilizing steel slag
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Contributing the hydrogen infrastructure formation by spreading usage of the specialized steel for hydrogen station
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Development and dissemination of Eco ProductsTM that contribute to reductions in CO2 emissions at the point of product use
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Development of Hydrogen Steelmaking Process for Zero Emission
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
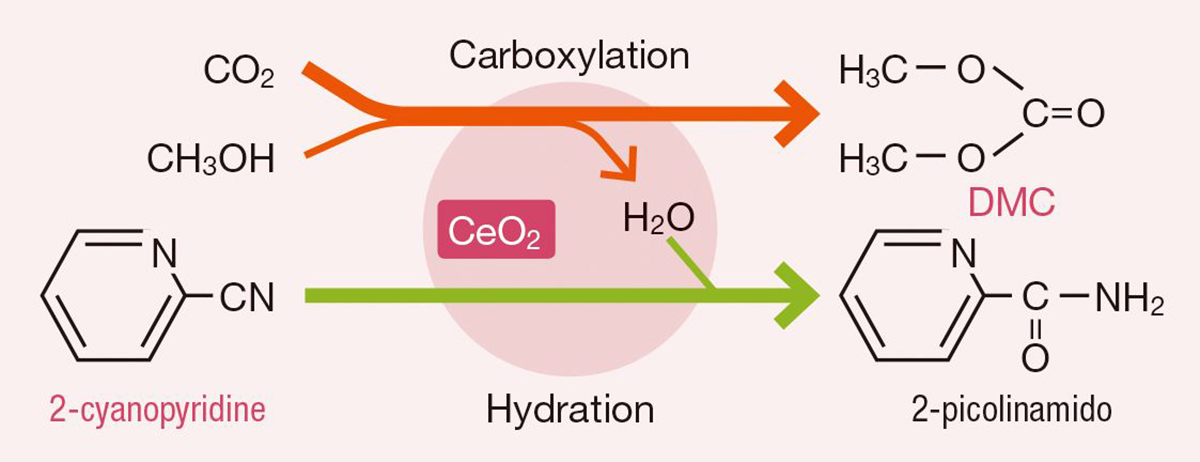
Establishment of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) production method using CO2 as raw material
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Provision of solutions for “National Resilience” aimed at adaptation to climate change
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
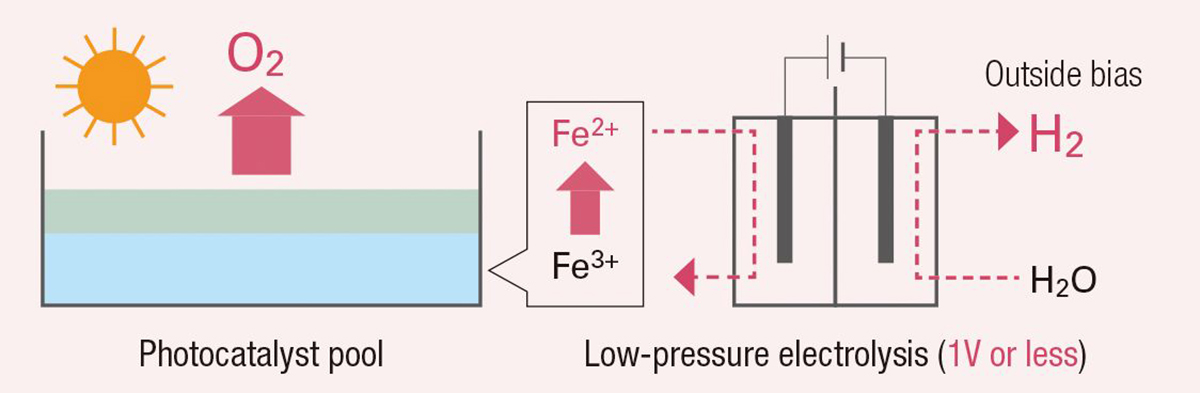
Zero emission hydrogen production technology by artificial photosynthesis
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
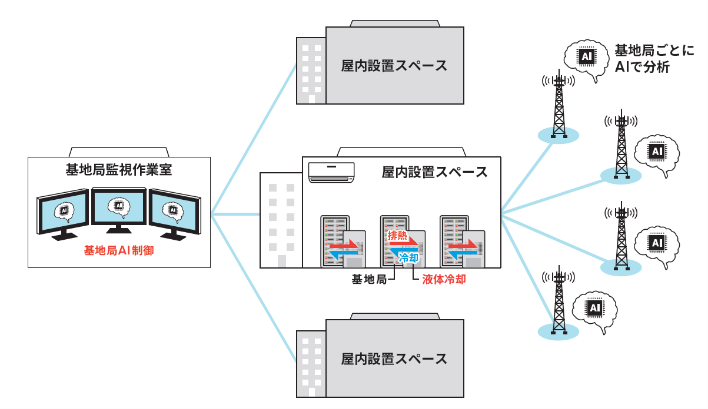
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION