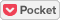Provision of solutions for “National Resilience” aimed at adaptation to climate change
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Outline
In recent years natural disasters have intensified in Japan and various disasters, including earthquakes, heavy rain, heavy snow, and volcanic eruptions, have caused severe damage to people’s lives. The Japanese Government has been promoting various measures by establishing the Fundamental Plan for National Resilience based on the Basic Act for National Resilience.
In this environment, the Nippon Steel Group is striving to enhance its technologies and products, which can contribute to National Resilience, and make proposals to clients (such as the government and municipalities) and design consulting firms. Particularly with regard to measures to counter tsunami and liquefaction, triggered by earthquakes, and fields involving the repair or reinforcement of agricultural facilities (such as water-use facilities and reservoirs), the Nippon Steel Group has been making steady achievements, including the adoption of its technologies and products.
Description
(1) Development
Given the condition of intensifying natural disasters and the government’s measures, we have decided to establish/strengthen our organization engaged in measures for National Resilience and to powerfully develop related nationwide group-wide activities. In fact, together with group companies, we formed a working group for National Resilience and launched cross-sectional initiatives to develop products that are more adapted to the government measures. By clearly presenting what types of solutions can be provided with our products for each disaster type or for each disaster-preventive measure, which differs by region or sector, we will make specific proposals and provide a wide range of solutions for National Resilience.
【Application by focused area】
・ Civil engineering area
1) Harbors, airports and fishing ports; 2) Seashore; 3) Rivers; 4) Control of erosion/sediment and landslides; 5) Agricultural water use; 6) Roads, railways and (bridges); 7) Energy
・ Construction area
1) Government buildings and hospitals; 2) Schools; 3) Stations and airports; 4) Offices; 5) Factories and warehouses; 6) Shops; 7) Housing; 8) Other
(2) Development of technologies, etc.
Among solutions for National Resilience, we develop products and methods that cope with natural disaster risks, such as earthquakes, tsunami, heavy rains and typhoons, and prevent /mitigate disasters in the civil engineering and architectural areas, jointly with universities, research institutions, architectural design firms, etc.
Some of the effective development examples to counter torrential rains that are assumed to be caused by climate change are presented below.
【Development examples】
(1) Reinforcement of embankments
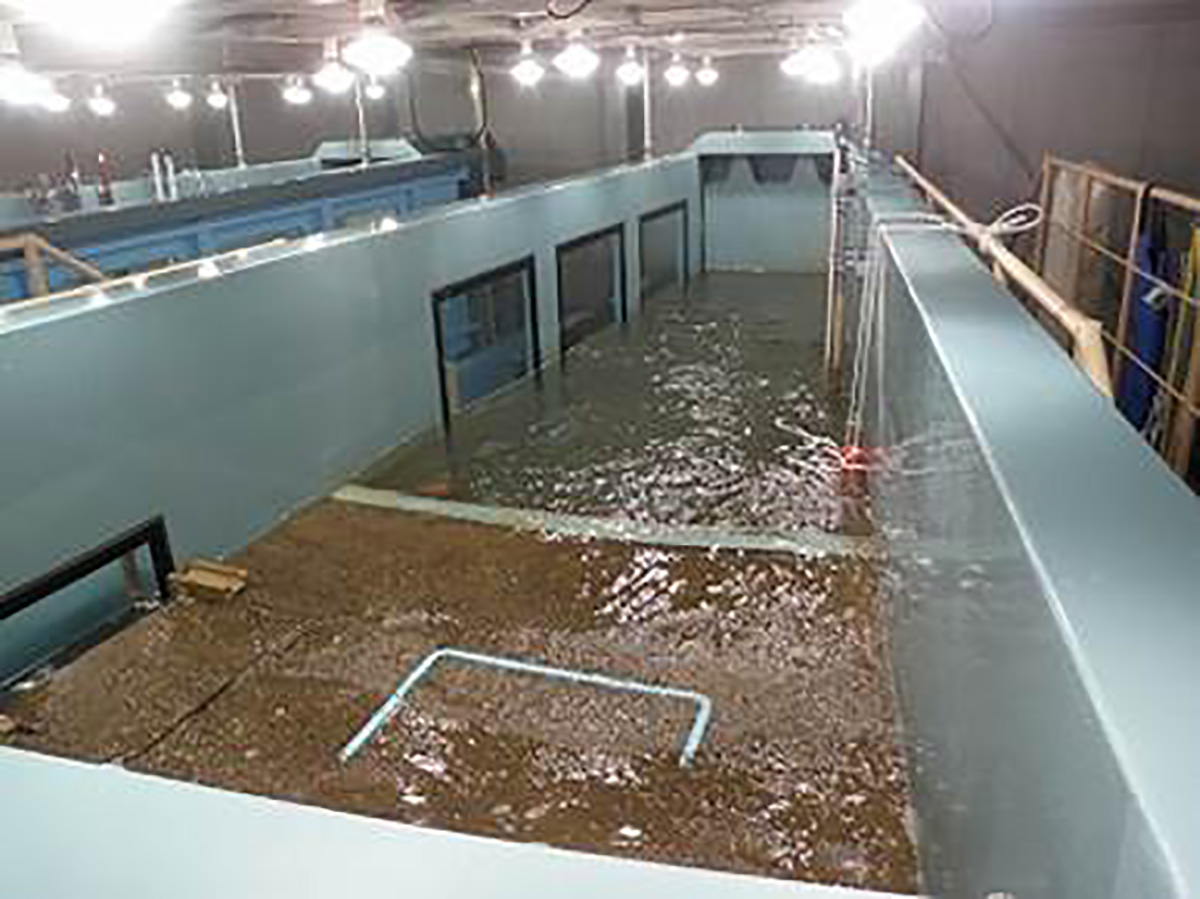
In order to prevent reservoirs that supply water for agricultural/domestic use from being destroyed by torrential rain or brief but heavy downpours, we are developing a new reinforcement method for embankments. This entails installing double steel sheet pile walls on the inner side of an onshore levee so as to sandwich the ground material that comprises the levee body. Specifically, we are verifying 1) the effects of the measure by using model experiments and numerical analyses (joint research with Kochi University) and 2) the securement of the height of the levee body, and the effects of blocking off seepage water in the case of adopting a reinforcement method using steel sheet piles in actual reservoir (jointly with Kochi Prefecture). Reinforcement of embankments by use of this method functions not only as a countermeasure against heavy rain but also as a method to prevent the levee body from being destroyed by liquefaction caused by an earthquake. This can potentially prevent human damage caused by the collapse of the levee body in over 60,000 reservoirs that are being forewarned of the danger out of 166,638 agricultural reservoirs across Japan.
We are also working on adopting this method for offshore levees. The risk of damage caused by high tides in coastal areas has increased due to a combination of rising sea levels, caused by climate change, and frequent strong typhoons. In order to prevent inundation damage in coastal areas, we intend to provide seashore embankment enhancement solutions by making use of the strong properties of steel to withstand enormous water pressure.
Due to an increase in strong typhoons and linear rainbands, which become stationary in local areas and bring unprecedented heavy rainfall, record-breaking torrential rain occurs more frequently in Japan, resulting in the bursting of water flows into rivers beyond their flow capacity level. In 2019, when the No. 19 Typhoon hit mainly in the Kanto and Tohoku regions, more than 140 river embankments collapsed, caused devasting damage to people and destroyed houses. We are also promoting the development of a method that uses resilient steel sheet piles to prevent the collapse of river embankments, as they tend to be made only of fragile soil materials, similar to reservoirs.
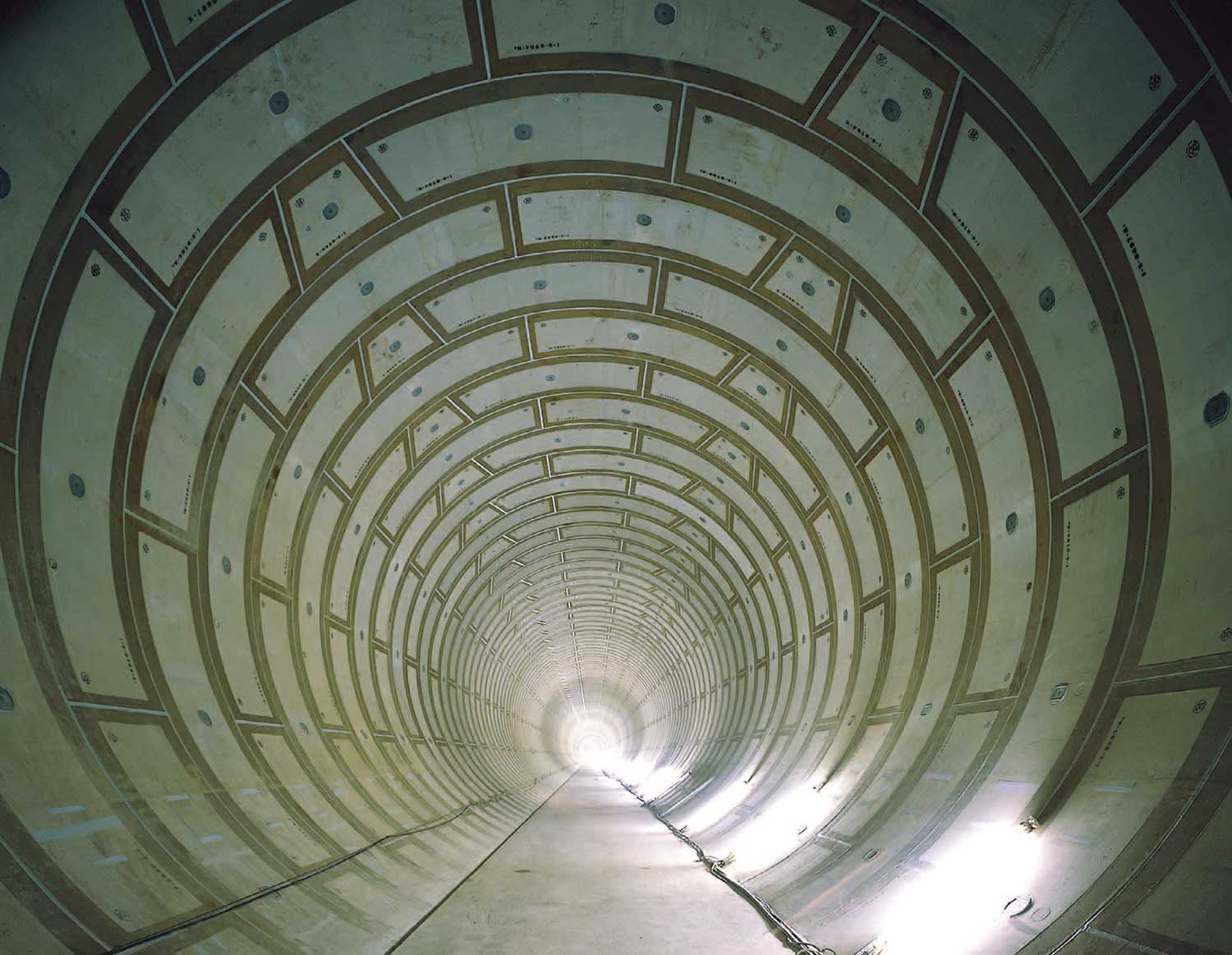
(2) Underground rivers
As a countermeasure of flood disaster due to frequent torrential rain, huge underground spaces (underground rivers) have been increasingly built by shield tunnel method in urban areas, where widening of rivers or reverbed excavation is difficult to carry out. Underground rivers are constructed by assembling segments connected with joints, which need to be capable of following the deformation caused by the compression force of earth pressure and the tensile force of internal water pressure.
The NM segment, which is a composite structure of steel and concrete, has original joints with superior deformation performance. We have been carrying out 1) strength tests of the segment; 2) full-scale joint strength tests to verify joint behavior under external/internal pressure; 3) development of an original sealing structure that can cope with high water pressure at deep underground, and tests of its sealing performance; and 4) development of inner anticorrosive materials with excellent resistance to abrasion and corrosion, and tests to confirm their durability.
Underground rivers comprised of NM segments have been adopted in major underground rivers in Tokyo and other areas. It is expected that the demand for them would grow as one of the countermeasures to intensified urban-type water disasters. We are taking up the challenge to develop more economical new segment in order to promote their further spreading.
(3) Control of erosion/sediment and landslides (Nippon Steel Metal Products Co., Ltd.)
・ Steel-slit dams: Structure that allows harmless sediment to flow downstream under normal conditions and effectively captures boulders and driftwood when a debris avalanche occurs.
・ NONFRAMETM: A method that stabilizes natural slopes by complementing natural slope vegetation effects while limiting the number of trees felled
Partner(s)
Municipalities, universities, relevant ministries/agencies, general contractors, consulting firms, architectural firms, etc.
Supplementary information
Nippon Steel Group’s Solutions for National Resilience (only in Japanese)
https://www.nipponsteel.com/product/kokudo_kyoujinka/
Other Innovation Challenges
CO2 uptake and carbon storage as blue carbon by utilizing steel slag
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Contributing the hydrogen infrastructure formation by spreading usage of the specialized steel for hydrogen station
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Development and dissemination of Eco ProductsTM that contribute to reductions in CO2 emissions at the point of product use
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Development of CO2 emission reduction technology using hydrogen in blast furnace steelmaking
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Development of Hydrogen Steelmaking Process for Zero Emission
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
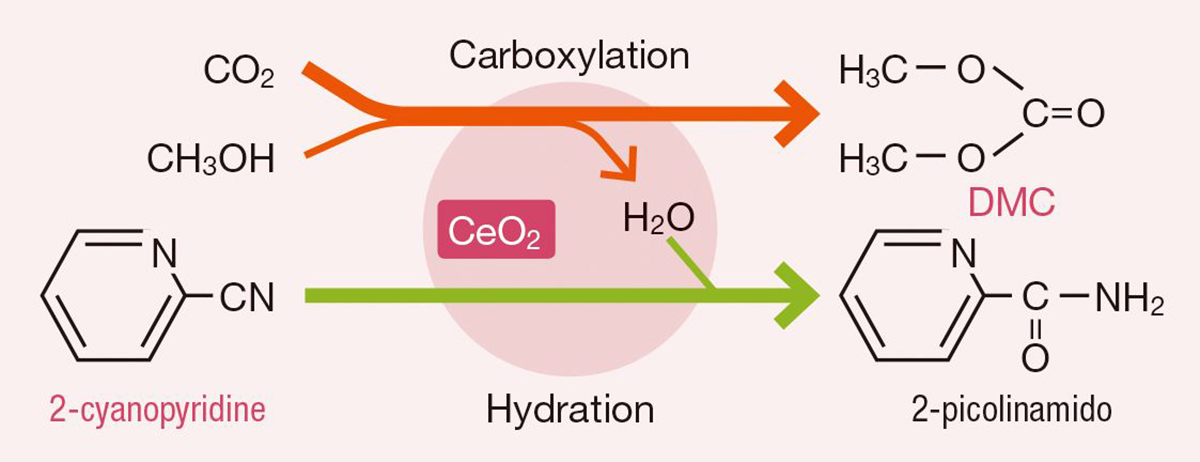
Establishment of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) production method using CO2 as raw material
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
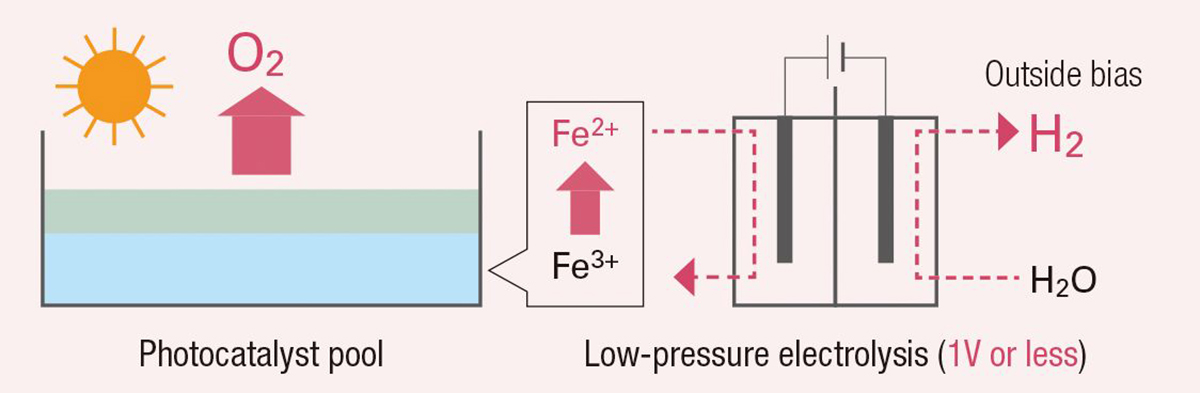
Zero emission hydrogen production technology by artificial photosynthesis
NIPPON STEEL CORPORATION
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION