Challenge to low-carbonization and decarbonization in city gas source using methanation-related technology
OSAKA GAS CO.,LTD.
Outline
In the short-to-medium term, Japanese city gas industries will contribute to achieving the 2030 goals target in global warming countermeasures and long-term energy supply and demand outlook, through the initiative for low-carbonization at the energy consumption stage by the shifts of energy to natural gas and the advanced utilization of natural gas. In the medium to long term, we will challenge to further low-carbonization and decarbonization through technical innovations such as methanation technology.
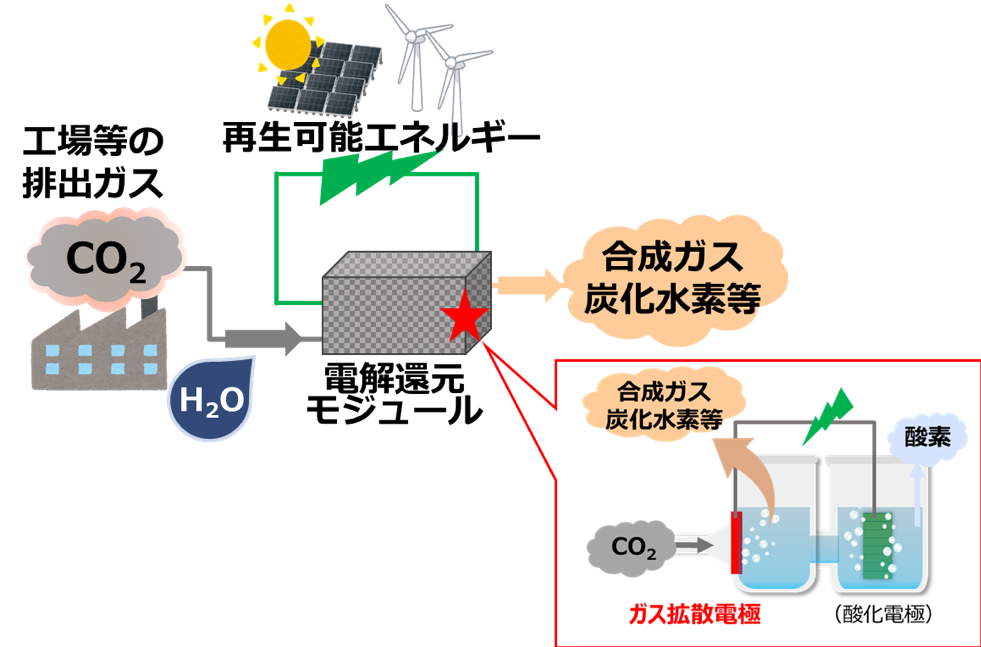
Methanation technology is a carbon recycling technology that produces methane, which is the main component of city gas, using CO2 and other materials as raw materials. By utilizing existing city gas infrastructure and customer-side facilities, this technology is expected method for decarbonizing of city gas can be reduced while reducing social cost.
Osaka Gas, in cooperation with the Japan Gas Association, will contribute to the development of methanation using "water electrolysis & Sabatier reaction technology" and "SOEC co-electrolysis & methanation reaction technology". In particular, the latter is expected to be a more efficient methanation technology without presupposing hydrogen distribution, and Osaka Gas is actively engaged in basic research through participation in NEDO's “Feasibility Research toward CO2 Effective Utilization Technology (CO2 Direct Decomposition)” project.
Description
In the government's “Innovative Environmental Innovation Strategy,” methanation-related technology is positioned as one of the 39 themes that are expected to have a significant greenhouse gas reduction effect. Since the generated methane is the main component of the city gas, the methanation technology uses existing city gas infrastructure and customer-side equipment to reduce social costs and lead to decarbonization. This is a technology expected to reduce greenhouse gases. Under such circumstances, Osaka Gas, in cooperation with the Japan Gas Association, is working on methanation using "water electrolysis / Sabatier reaction technology" and "SOEC co-electrolysis / methanation reaction technology". Regarding the latter technology in particular, Osaka Gas has been jointly adopted in July 2019 with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) as a contract research organization for “Feasibility Research toward CO2 Effective Utilization Technology (CO2 Direct Decomposition)” project (FY2019-2020) of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), and is working on basic research.
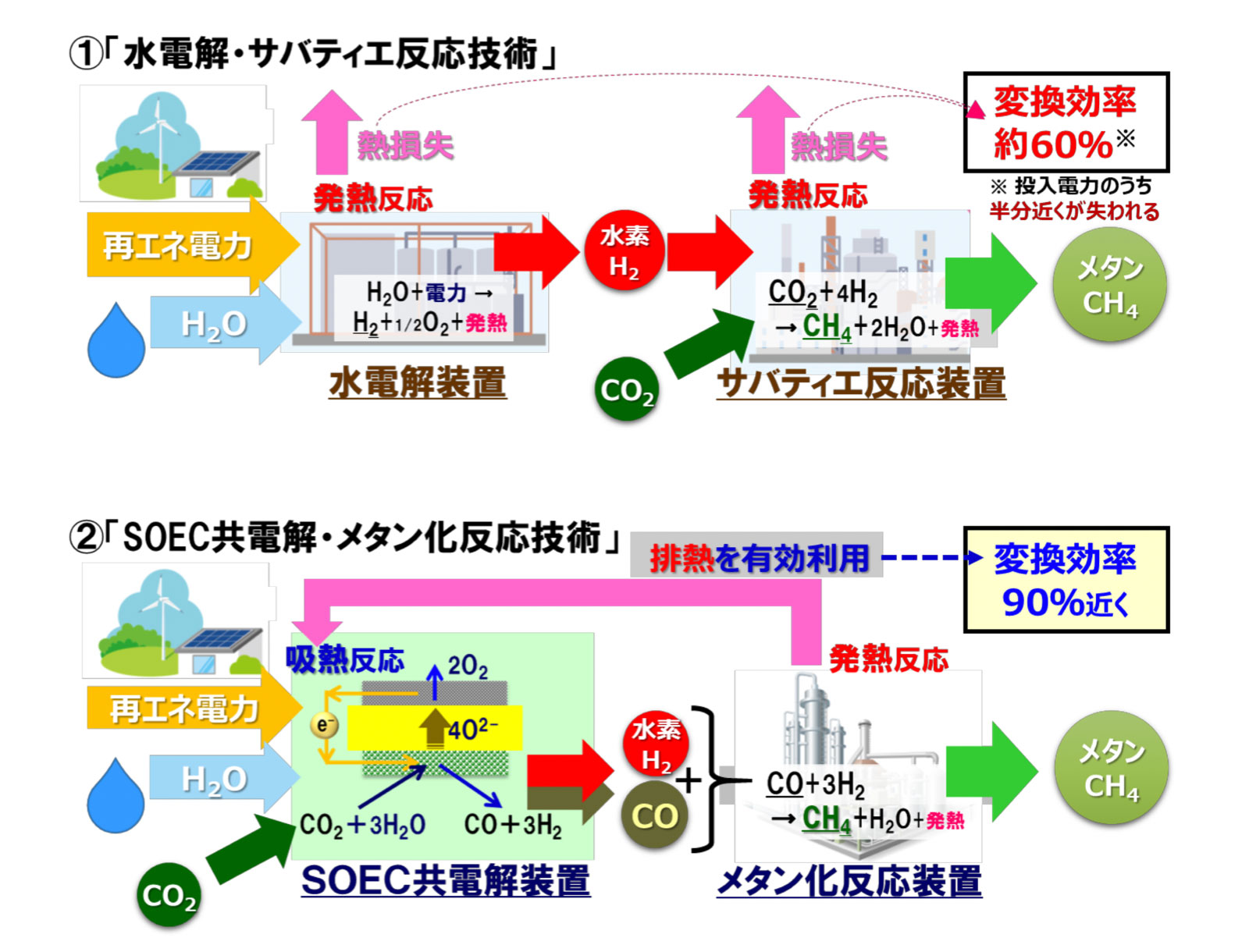
(1) "Water electrolysis / Sabatier reaction technology"
This technology synthesizes methane by the "Sabatier reaction※" using hydrogen obtained by electrolyzing water with renewable energy powers and CO2 captured by various CO2 capture technologies.
※ "Sabatier reaction" is the reaction of CO2 and H2 over a catalyst to produce CH4, and the reaction equation is expressed as follows;
CO2 + 4H2 -> CH4 + 2H2O.
Although the basic technical elements of this technology have already been established, in order to put it into practical use, there are several technical issues such as the establishment of technology to control the generated reaction heat, the improvement of the durability of the catalyst, the design of the methanation reactor, and the downsizing of the systems, etc.
Osaka Gas is contributing to future social implementation of this technology in cooperation with the Japan Gas Association, such as creating a technology development roadmap and considering commercialization / construction of large-scale plants in the future. The Japan Gas Association plays a leading role in the Organization for Carbon Capture & Reuse (CCR), which also includes companies that are conducting demonstration tests of this technology.
(2) "SOEC co-electrolysis / methanation reaction technology"
This technology uses SOEC*1 to generate hydrogen and CO by electrolysis (co-electrolysis*2) of CO2 together with steam using renewable energy power, etc., and synthesizes CH4 by methanation reaction*3.
*1 Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell. Reverse functional device of SOFC (Solid Oxide Fuel Cell).
*2 The reaction equation of the co-electrolysis reaction is expressed as follows;
CO2 + 3H2O (+electric power) -> CO + 3H2 (+O2), (Endothermic reaction).
*3 The reaction equation of the methanation reaction is expressed as follows;
CO + 3H2 -> CH4 + H2O, (Exothermic reaction).
In this technology, since the heat generated in the methanation reaction (exothermic reaction) can be effectively used by the SOEC co-electrolysis reaction (endothermic reaction), the power required for co-electrolysis is reduced, and the energy conversion efficiency of this technology is higher than that of “water electrolysis / Sabatier reaction technology”. Further, there is a feature that there is no need to supply hydrogen.
In this way, "SOEC co-electrolysis / methanation reaction technology" is theoretically very efficient and has many advantages, but there are many technical issues to be solved and it can be said that it is still in the basic research stage.
Therefore, in order to clarify the potential of this technology and the issues to be addressed, Osaka Gas is conducting NEDO's “Feasibility Research toward CO2 Effective Utilization Technology (CO2 Direct Decomposition)” project (FY2019-2020) in collaboration with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, has begun basic research on technical issues such as improving the co-electrolytic performance of SOEC and controlling the methanation reaction.
In addition, we are collaborating with the Japan Gas Association to discuss the verification of the advantage of "methanation utilizing co-electrolysis technology".
After mass introduction and cost reduction of renewable energy power and cost reduction of large-scale intensive CO2 capture method are established, and if the cost and stability of city gas production by methanation are no longer inferior to those of city gas production from other source, we assume that the gas by methanation will be supplied to customers, and aiming at the commercialization of “methanation utilizing co-electrolysis technology”, we will challenge on basic research and survey of necessary technologies and the realization of demonstration tests.
Partner(s)
New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
The Japan Gas Association
Organization for Carbon Capture & Reuse (CCR) , https://ccr-tech.org/en/
Other Innovation Challenges
Dissemination of Compact Hydrogen Generator for On-site Hydrogen Filling Station
OSAKA GAS CO.,LTD.
R&D and spread of ENE-FARM, a residential fuel cell system toward hydrogen economy
OSAKA GAS CO.,LTD.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.



-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)