CO₂ Methanation
INPEX CORPORATION
Outline
INPEX is currently involved in the development of methanation technology as one of the company's core technologies. The company strives to create technologies transforming electricity into hydrogen, hydrogen into methane and methane into electricity, as well as build an "electricity-hydrogen-methane value chain" that incorporates INPEX's existing methane production and transportation system.
Methanation is a technology used to convert carbon dioxide into valuable resources like methane. INPEX has been participating as a contractor in a project sanctioned by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) to develop technologies to effectively utilize CO₂. As part of this initiative, INPEX is involved in the evaluation of the technological development and production sequence of a carbon capture and utilization (CCU) technology that produces and effectively utilizes methane using a high concentration of CO₂ emitted from thermal power plants and hydrogen produced using electricity derived from renewable energy sources.
Description
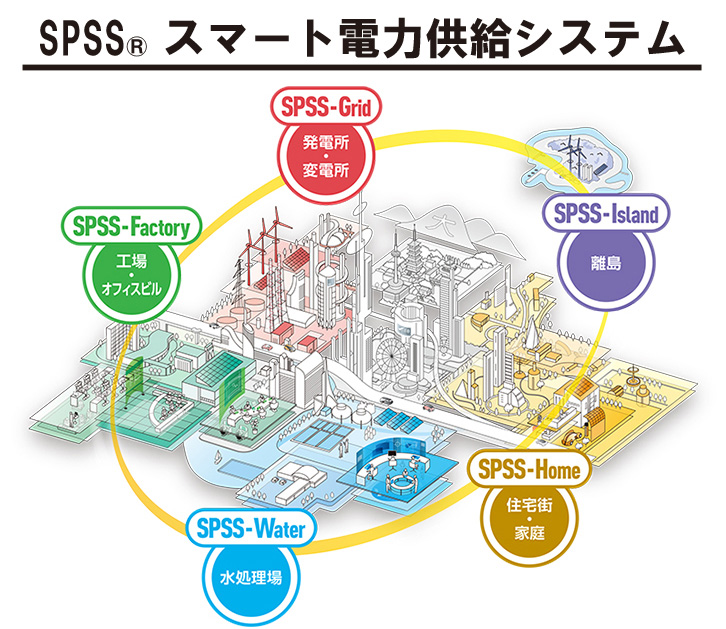
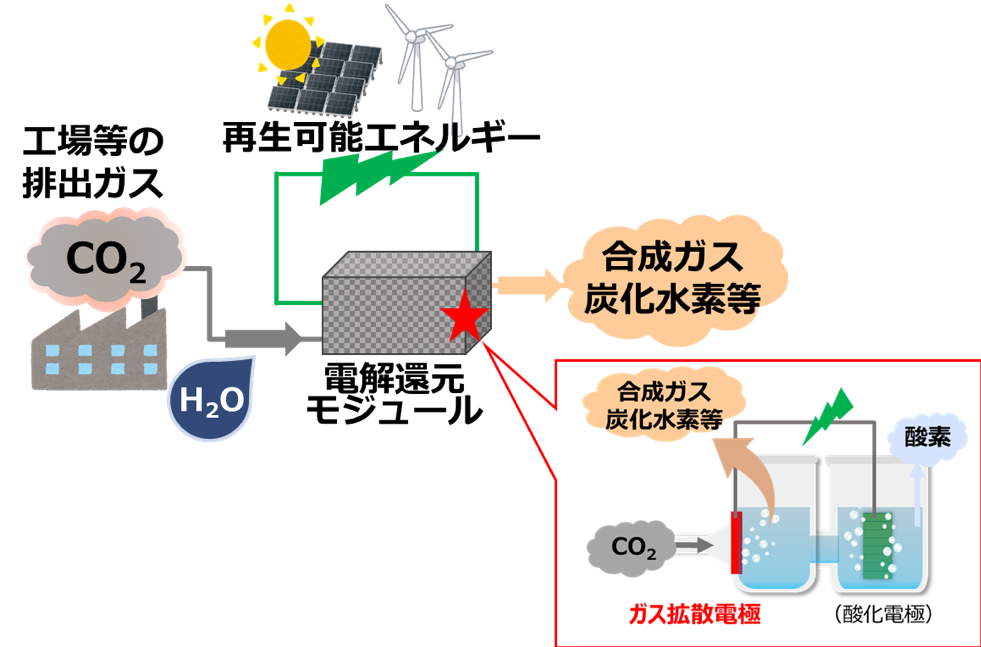
CO₂-methanation involves a three-step process. First, electricity derived from renewable energy sources (including variable and non-variable) produces green hydrogen derived from renewables by electrolysis of water. Second, the produced hydrogen and a high concentration of CO₂ emitted from coal-fired power plants, etc., or associated CO₂ emitted from INPEX’s own natural gas production process are converted to methane derived from renewables by a CO₂-methanation system. Finally, the converted methane is introduced to INPEX’s existing supply chain consisting of natural gas and city gas supplied as LNG and through pipelines. Through this process, INPEX aims to build a network-type, low-carbon energy supply system.
Ultimately, the reduction of additional CO₂ will become possible by replacing methane derived from natural gas and/or city gas with the same amount of methane derived from renewable energy sources. In other words, while CO₂ will be emitted from the combustion of methane derived from renewable energy sources, CO₂-methanation is expected to contribute to net zero carbon as a carbon recycling technology, as the CO₂ is initially separated, recovered and used in the same way as biomass-derived fuel.
Currently, the CO₂-methanation technology being developed as part of NEDO’s efforts to develop technologies to effectively utilize CO₂ is slated to become widely available by around 2050, as outlined in the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry's "Carbon Recycling Technology Roadmap (formulated on June 17, 2019)" and the Japanese Cabinet Office's "Innovative Environmental Innovation Strategy (formulated on January 21, 2020)." However, the roadmap targets the technology’s commercialization in around 2030 from the viewpoint of technological development.
It is envisioned that this commercialization in around 2030 will be enabled by the construction of a facility with the capacity to convert one million tons of CO₂ per year (60,000 Nm3-CO₂ per hour) into methane as one unit. On the other hand, the capacity of the CO2-methanation test facility currently being used is limited to a basic technology development scale of 8 Nm3-CO₂ per hour. Therefore, a phased technological development scheme is required to reduce cost by scaling up capacity to 7,500 times the current level to reach the envisioned commercial scale.
In addition, through the ongoing CO₂-methanation technology development outlined above, INPEX and the Australian Federal Institute for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIRO) are implementing a commercial-scale Pre-FS project as the first initiative based on the Japan-Australia Carbon Recycling Cooperation Memorandum (concluded on September 25, 2019) signed between the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan and the Australian Ministry of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources (DISER).
Partner(s)
New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)
Hitachi Zosen Corporation
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Nagoya University
Other Innovation Challenges
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.


-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)