Energy saving and reduction of CO2 emissions by PVC windows
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Outline
PVC resin is made from 60% salt and 40% petroleum, and its manufacturing energy is about 60% that of other resins, making it a product with low environmental impact. PVC resin raw materials manufactured and supplied by Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. are processed by resin processing manufacturers, have excellent durability and weather resistance, and are easy to recycle; therefore, they are widely used for various applications. In particular, PVC resin windows (hereafter referred to as “PVC windows”) have excellent heat insulation, airtightness, sound insulation and dew condensation prevention properties, and they have become the mainstream in developed countries in Europe and the United States to allow for a more comfortable living environment. For detached houses, 70% of the heat enters the room through openings such as windows during cooling in summer, and 60% of the heat escapes from openings during heating in winter. Therefore, in Japan, too, the adoption of PVC windows has progressed mainly in cold regions, contributing to energy conservation and reduction of CO2 emissions. Japan has set a future target of a 40% reduction in CO2 emissions in the household sector from FY 2013 levels, and the Company hopes to contribute to energy conservation and CO2 emissions reduction by further promoting the use of PVC windows.
Description
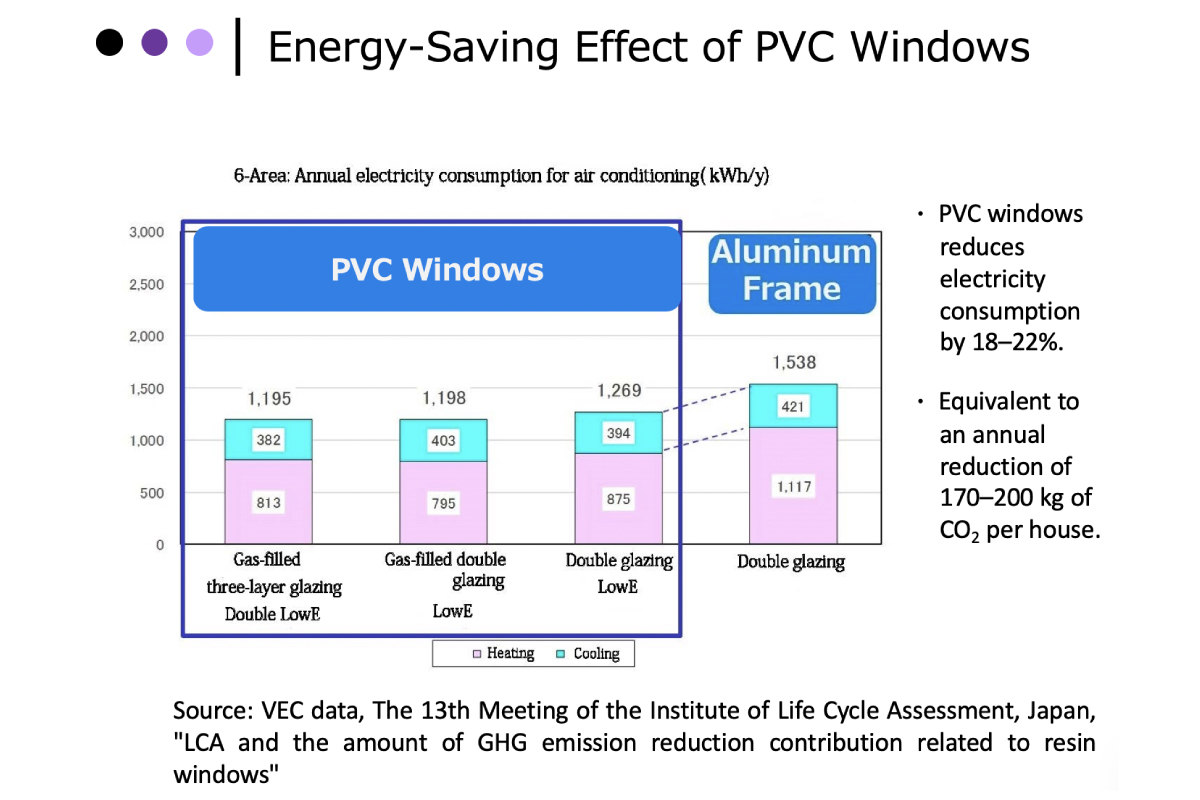
We verify the CO2 reduction effect of PVC windows for a standard detached house as shown in Table.1.
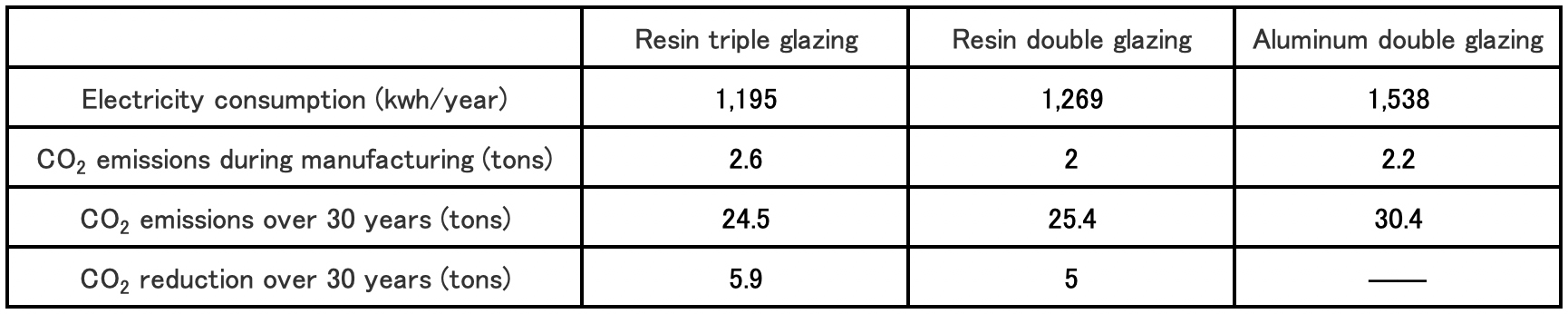
As shown in Table.2, annual electricity consumption per house can be reduced by 18% to 22% by using PVC windows. The superiority of PVC windows has also been demonstrated in a comparison of total CO2 emissions from manufacturing to disposal over 30 years of use.
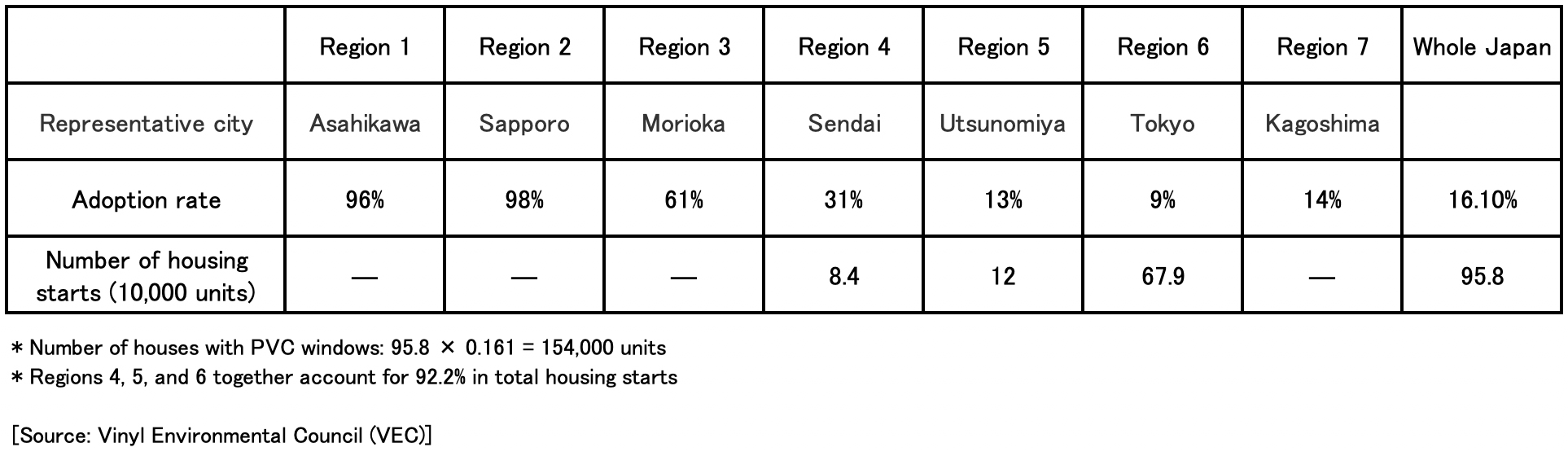
Based on Table-2 and Table-3, of the 958,000 houses that started construction in 2016, 154,000 houses with PVC windows are estimated to reduce CO2 emissions by 430,000 tons to 950,000 tons over the next 30 years, taking into account the U-value (heat transfer coefficient). Based on the volume of shipments, the amount of CO2 emissions reduction attributable to PVC resin produced by the Company is 260,000 tons to 570,000 tons. Although the number of housing starts in Japan is expected to decrease in the future, we would like to contribute to energy conservation and CO2 reduction in the household sector by promoting the spread of PVC windows in Regions 4, 5 and 6 with a lower adoption rate of PVC windows and a higher number of housing starts compared to cold regions. At the same time, we intend to actively promote the use of PVC windows in hospitals, nursing homes, elderly care facilities, and other facilities to conserve energy and protect people's lives and health from heat shock.
Partner(s)
Resin windows manufacturers
Housing manufacturers
Vinyl Environmental Council
Other Innovation Challenges
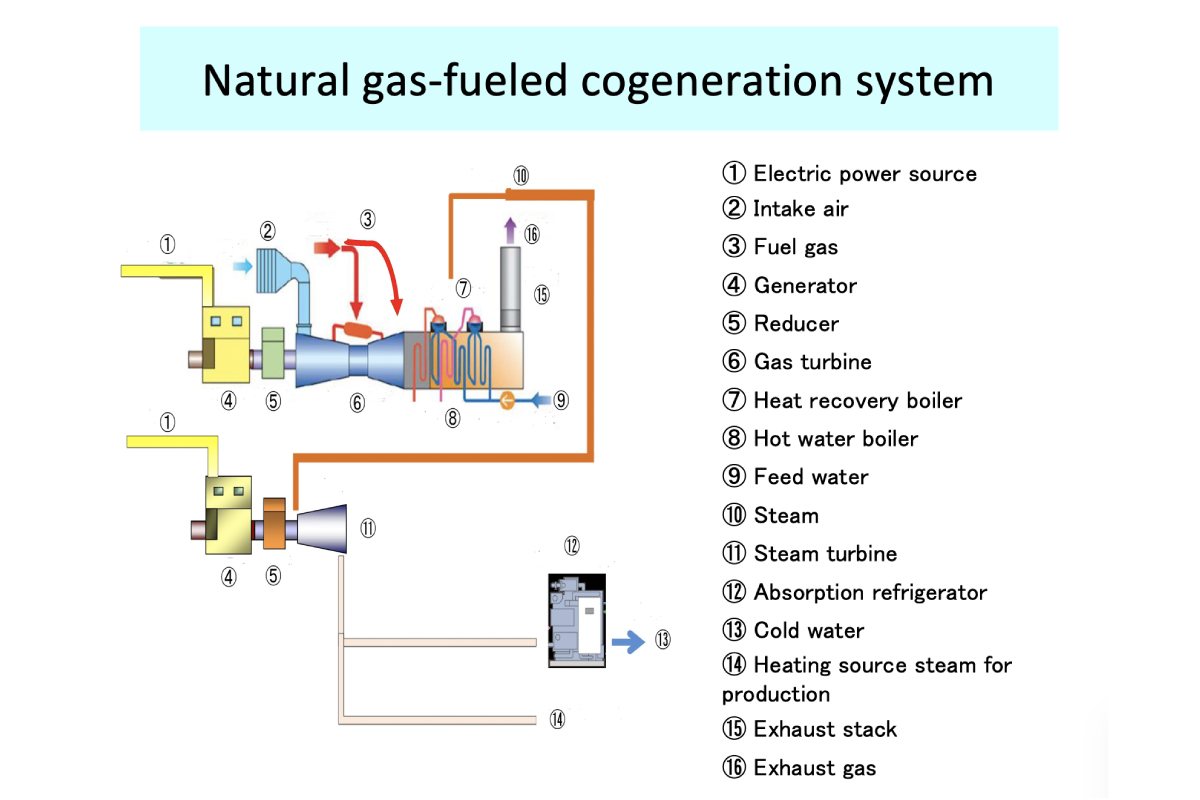
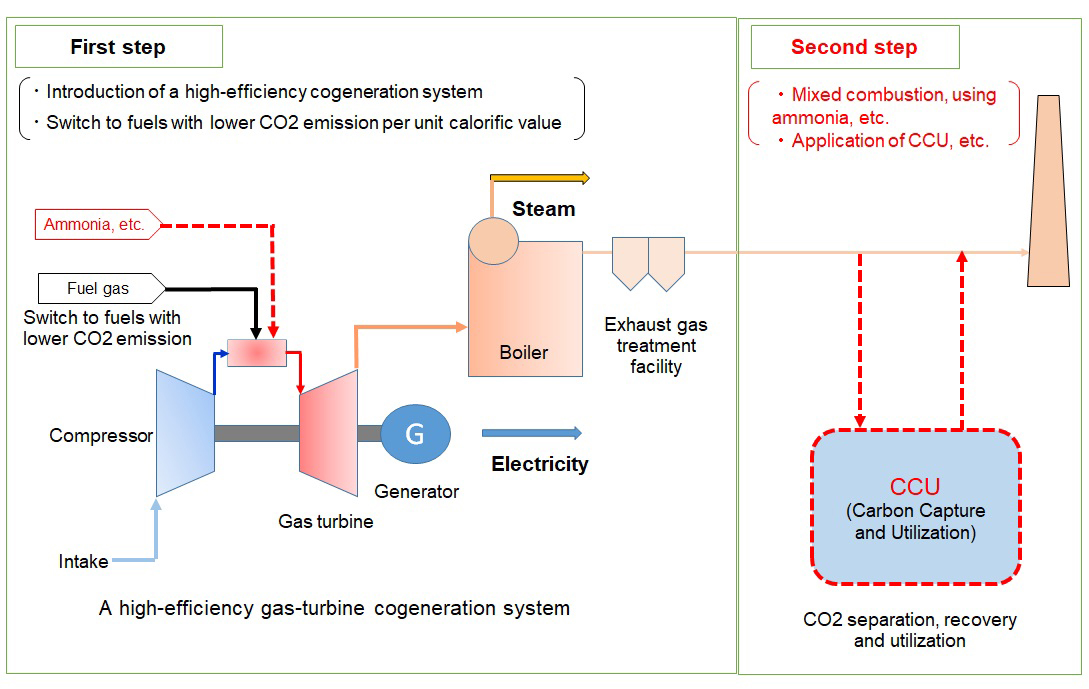
Reduction of CO2 gas by highly efficient gas cogeneration
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
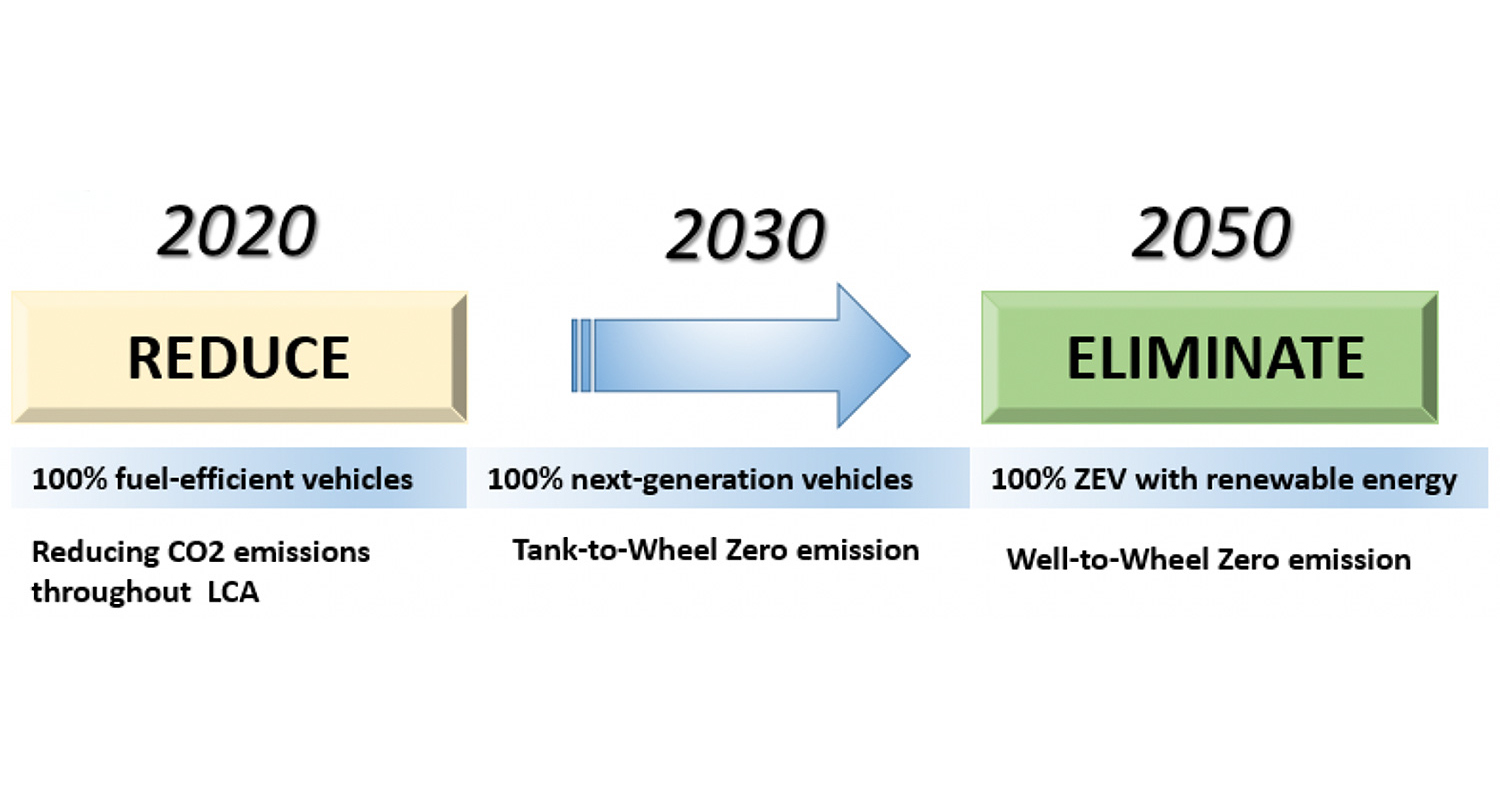
Achieve 2050 decarbonization target with Net Zero Energy House!
Sekisui House, Ltd.
Achieving net-zero emissions by promoting renewable energy use through both our monozukuri and products.
DAIWA HOUSE INDUSTRY CO., LTD.