Reuse and Recycling of Electric Vehicle Batteries
JERA Co., Inc.
Outline
With the recent popularization of electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles, the number of used batteries from electric vehicles (hereinafter referred to as “battery”) is expected to grow in the near future. At present, although some batteries are reused on a small and limited scale, most of them are not reused and are incinerated for recycling, and the residue is smelted and extracted.
In addition, storage batteries are expected to be used as a variety of tools, such as for the purpose of decarbonizing electricity by renewable energy, for the purpose of adjusting supply and demand for local production and local consumption of energy systems, for the rationalization of thermal power generation operations, and for BCP applications.
In order to effectively use the abundant battery resources, our company will reuse the EV batteries in the electric power system. Also, considering economic efficiency and CO2 emission reduction, our company will develop new battery recycling technologies without incineration. These actions will lead to a low-carbon and recycling society.
Description
Reuse
As electric vehicles are expected to become more popular in the future, our company aims to reuse batteries collected from electric vehicles as an energy storage system. Even if the battery recovered from the electric vehicle has deteriorated, by combining a large number of batteries and appropriately controlling them, it is possible to use them to adjust supply and demand in line with the expansion of the introduction of renewable energy and to respond to frequency fluctuations, which contributes to reasonable operation of thermal power plants.
However, for further expansions of secondary use of batteries, there are problems in estimating battery life and evaluating the value and reliability of the used storage batteries. In order to solve these problems, we are conducting joint development of technology to utilize batteries in electric power systems with Toyota Motor Corporation, which leads technological development such as efficient selection, safe use of low performance batteries and different performance batteries, and long-term operation. By establishing this technology, we aim to build an energy storage system that can easily incorporate different types of batteries regardless of the manufacturer or type of battery.
As a concrete effort, a small-scale reused storage battery system utilizing reused batteries is being constructed, and the operation of each device combination is verified, problems as a system are identified, and utility optimization and control methods are sought. From the studies conducted so far, it has been confirmed that the reused storage battery system has the function of adjusting supply and demand and responding to frequency fluctuations.
As the next step, we will aim to build a facility structure that matches the type and volume of the reused batteries in the future, such as by combining nickel-hydrogen batteries and lithium-ion batteries, which have different characteristics as batteries, and we will study ways to expand the range of reusing batteries.
Recycling
The batteries use rare earths such as nickel and cobalt, which are imported. At present, the method generally used to recycle batteries is smelting and extracting of nonferrous metals after incineration, in order to easily detoxify the energy accumulated in the battery. However, in order to secure rare earths for the future era of mass introduction of storage batteries, it is necessary to improve the efficiency of recycling technology and to recycle them without incineration from the viewpoint of CO2 reduction. Therefore, our company is establishing new recycling processes that are highly efficient and can reduce CO2 emissions.
As a concrete measure, we are developing recycling methods and processes for both nickel-hydrogen batteries and lithium-ion batteries without incineration.
As for nickel-hydrogen batteries, the feasibility of each elemental technology was confirmed through laboratory tests, and a pilot plant was constructed and verified, and it was confirmed that the recycling process was established.
We also verified the elemental technologies of lithium-ion batteries and confirmed that recycling methods similar to those of nickel-hydrogen batteries can be applied. On the other hand, it is necessary to establish a safe and optimum pretreatment method for lithium-ion batteries, and the methods of cutting and crushing the batteries and extracting the electrolyte needs to be verified. Furthermore, we will expand the recycling range by establishing a technology for recovering lithium contained in electrolyte.
In the future, through the establishment of new battery recycling methods that do not involve incineration and the improvement of material recovery rates, we aim to stabilize the procurement of rare earths in Japan, to reduce CO2 emissions compared with conventional methods, and to contribute to the popularization and expansion of electric vehicles.
Partner(s)
Toyota Motor Corporation
Supplementary information
1. Demonstration of Electric Vehicle Batteries Reuse and Recycling
https://www.chuden.co.jp/corporate/publicity/pub_release/press/3266975_21432.html
2. FY 2018 Report on Demonstration Project of Equipment Technology for CO2 Reduction Recycling
http://www.env.go.jp/recycle/car/pdfs/h30_report01_mat06.pdf
3. Materials presented by the Working Group for the Promotion of Reuse of In-Vehicle Batteries of the Electric Motor Vehicle Utilization Society
(Utilization of Reused Batteries for Electric Vehicles in Electric Power Systems)
http://www.cev-pc.or.jp/xev_kyougikai/xev_pdf/xev_kyougikai_wg02-1_jera.pdf
Other Innovation Challenges
Development of high-efficiency thermal power plants and renewable energy sources
JERA Co., Inc.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
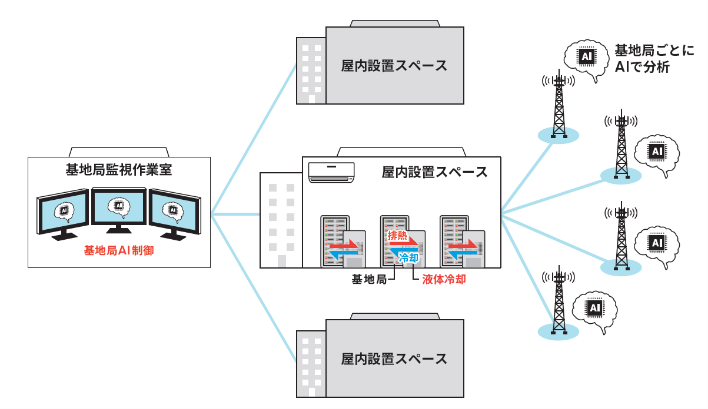
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION