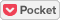Challenge for Zero-makeup water for cooling water system
KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Outline
1. Goal
Using high-quality process wastewater as the makeup water for industrial cooling water systems with cooling towers, thereby eliminating the need for the production of fresh water and the treatment of process wastewater that would emit CO2
2. Methods
(1) Reusing high-quality process wastewater from a plant for its cooling water system with minimal property modification. Selecting high-quality wastewater by applying water pinch technology to optimize water reclamation
(2) Applying concentration management, technologies for preventing fouling, and monitoring technologies including ones for monitoring the amount of reclaimed water and the water balance, for the purpose of getting further performance from a cooling water system while also reducing labor
(3) Building a system that enables labor reductions, in view of the process from the process wastewater to the cooling water system
Description
1. Background
In the industrial world, cooling water systems with cooling towers (hereafter, “cooling water systems”) are used widely for removing residual heat. Those systems are also generating a way to save water by means of water recycling.
On the other hand, there has yet to be an attempt to save makeup water, the water that is fed into the cooling tower to prevent excessive concentration caused by evaporation from cooling tower and recycling.
Makeup water is 5% to 20% of the water intake at ordinary plants. Saving makeup water is a promising potential way to reduce water consumption with relatively low risk. At some plants, general wastewater or process wastewater is already reused as makeup water. However, there are cases where cooling efficiency is lowered due to contaminants in the water.
2. Estimations
According to statistics on plants with 30 or more workers each (2014 industrial statistics from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry of Japan), the amount of water used for cooling and temperature adjustment is approx. 98,000,000 m3/day, and most of the water is estimated to be recycled water (reclaimed water).
Assuming that the amount of makeup water for cooling water systems accounts for 2% of the above, the annual amount of fresh water consumption is:
98,000,000 m3/day × 0.02 × 360 days/year = 705,600,000 m3/year (1)
Here, if the CO2 emission factor per 1m3 of fresh water is 0.36kg-CO2, the amount of CO2 emitted (the reduction potential) is estimated to be:
705,600,000 m3/year x 0.36 kg-CO2/m3 = 254,000 t-CO2/year (2)
3. Initiatives
1) Using no fresh water as makeup water for the cooling water system
Selecting high-quality water from process wastewater generated in a plant, and reusing it as makeup water for the plant’s cooling water system with minimal property modification. This will eliminate CO2 that would be emitted by the production of freshwater for the cooling water system and by the treatment of process wastewater that would be an amount equivalent to the freshwater.
High-quality wastewater is selected by applying water pinch technology as a method for optimizing water reclamation, to reduce risks of fouling from the reuse of wastewater while minimizing energy consumption for property modification.
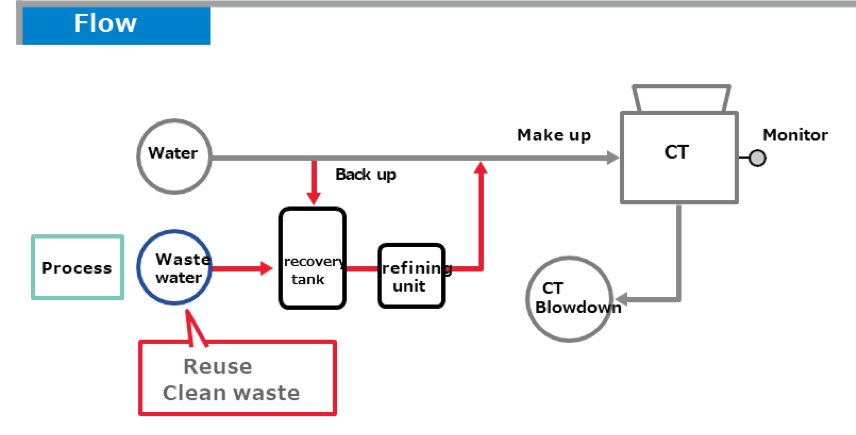
2) Implementing antifouling measures for the cooling water system (cooling tower and heat exchanger)
Making the performance of the cooling water system higher than when fresh water is used by applying concentration management, technologies to prevent fouling, and monitoring technologies including ones for monitoring the amount of reclaimed water and the water balance, thereby contributing to improving the productivity of the plant. At the same time, building a system covering the process from process wastewater to the cooling water system, thereby saving labor related to water reclamation and water treatment.
Other Innovation Challenges
Challenge for deploying Methane Fermentation Biogas Business
KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieve 2050 decarbonization target with Net Zero Energy House!
Sekisui House, Ltd.
Achieving net-zero emissions by promoting renewable energy use through both our monozukuri and products.
DAIWA HOUSE INDUSTRY CO., LTD.