Construction of virtual power plant (VPP) using electric vehicles
MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORPORATION
Outline
Since FY2018, Mitsubishi Motors Corporation(MMC) has been working with five companies in a demonstration project to establish a VPP utilizing customer-side energy resources.
In recent years, issues that affect the stable operation of the power system, such as output fluctuations due to renewable energy such as solar power generation and generation of surplus power, have become apparent. The construction of a VPP is being promoted as a new mechanism to achieve both low cost and continuous introduction of renewable energy and stabilization of the power system.
This demonstration project aims to achieve both continuous introduction of renewable energy and stabilization of the power system by using electric vehicles such as EVs (electric vehicles) / PHEVs (plug-in hybrid vehicles) as VPP resources.
From FY2021, MITSUBISHI MOTORS will establish a business model for the V2G (Vehicle to Grid) business that adjusts power supply and demand in both directions between the power system and electric vehicle storage batteries, and considers commercialization.
Description
MMC conducted a demonstration project in Japan in FY2018 and FY2019 in cooperation with five companies, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., TEPCO Energy Partner, Inc., TEPCO Power Grid, Inc., Hitachi Systems Power Services, LTD., and Shizuoka Gas Co., Ltd.
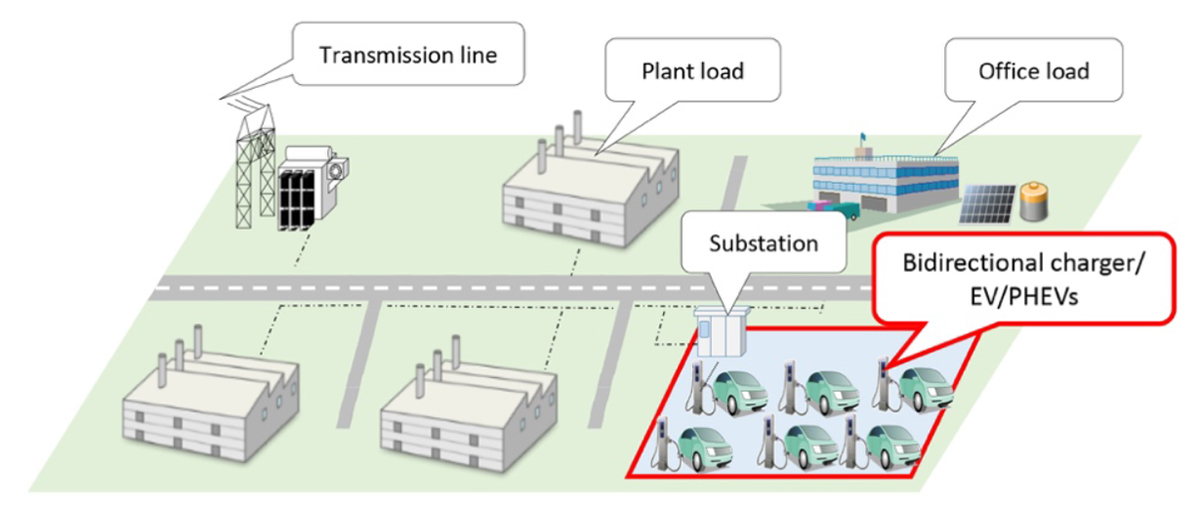
In the demonstration project, we will build a demonstration environment that enables bidirectional power interchange between electric vehicles and the power system. Furthermore, the electric vehicles parked at the demonstration site were simultaneously controlled on the online system, and the effectiveness of VPP, which contributes to the stabilization of the power system, was confirmed.
VPP is a mechanism that connects dispersed energy resources such as photovoltaic power generation facilities and storage batteries via a network so that they function as if they were a single power plant. One of these technologies, V2G, is a technology that utilizes in-vehicle batteries, such as electric vehicles, to supply stored power to the power grid in addition to charging.
As a result of the rapid introduction of renewable energy such as photovoltaic power generation, various issues affecting the stable operation of the power system, such as output fluctuations and excess power generated by renewable energy, are becoming apparent. In order to stabilize the power system, the construction of VPP is expected as a new social mechanism to achieve both low cost and continuous introduction of renewable energy and stabilization of the power system.
In this demonstration project, a V2G-compatible bidirectional charger was introduced on the demonstration site, and the largest demonstration environment in Japan was established to realize bidirectional power interchange between the electric vehicle and the power system. We conducted verification and confirmed its effectiveness in contributing to power system stabilization.
As an example of the demonstration, after establishing a station with a centralized arrangement of electric vehicles and bidirectional chargers for electric vehicles on the demonstration site, assuming the high-voltage lines on the premises as virtual distribution lines, control verification for stabilization was performed. In addition, electric vehicles parked at the demonstration site were simultaneously controlled on the online system, and issues were identified.
We will continue to promote the introduction of renewable energy by effectively using electric vehicles as storage batteries, and work to build a business model that allows V2G to function in society with the aim of solving energy and environmental issues.
Partner(s)
Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., TEPCO Energy Partner, Inc., TEPCO Power Grid, Inc., Hitachi Systems Power Services, LTD., Shizuoka Gas Co., Ltd.
Supplementary information
■ Mitsubishi Motors’ press release
Commencement of V2 G Experiment that Leverages Electric Vehicles as Resources for Virtual Power Plants
~Grant Received to Cover Costs of Virtual Power Plant Construction Demonstration Project that Utilizes Demand-side Energy Resources (V2G Aggregator Project)~ 2019/06/03
https://www.mitsubishi-motors.com/en/newsrelease/2019/detail1190.html
■ Mitsubishi Motors’ press release
Implementation of Demonstration to Prove the Feasibility of V2G Aggregators
~17 EV/PHEV used to implement Japan's largest EV power station experiment to demonstrate power grid stability~ 2019/03/01
https://www.mitsubishi-motors.com/en/newsrelease/2019/detail1165.html
■ Mitsubishi Motors’ press release
V2G Demonstrator Project Using EVs as Virtual Power Plant Resource
Awarded by METI to receive "Grants for Demonstrator Project for Virtual Power Plant Utilizing Consumer Energy Resources (VG2 Aggregator Project)" 2018/06/06
https://www.mitsubishi-motors.com/en/newsrelease/2018/detail1124.html
Other Innovation Challenges
Create a system that can quickly provide MMC electric vehicles to disaster-stricken areas in the event of a disaster
MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORPORATION
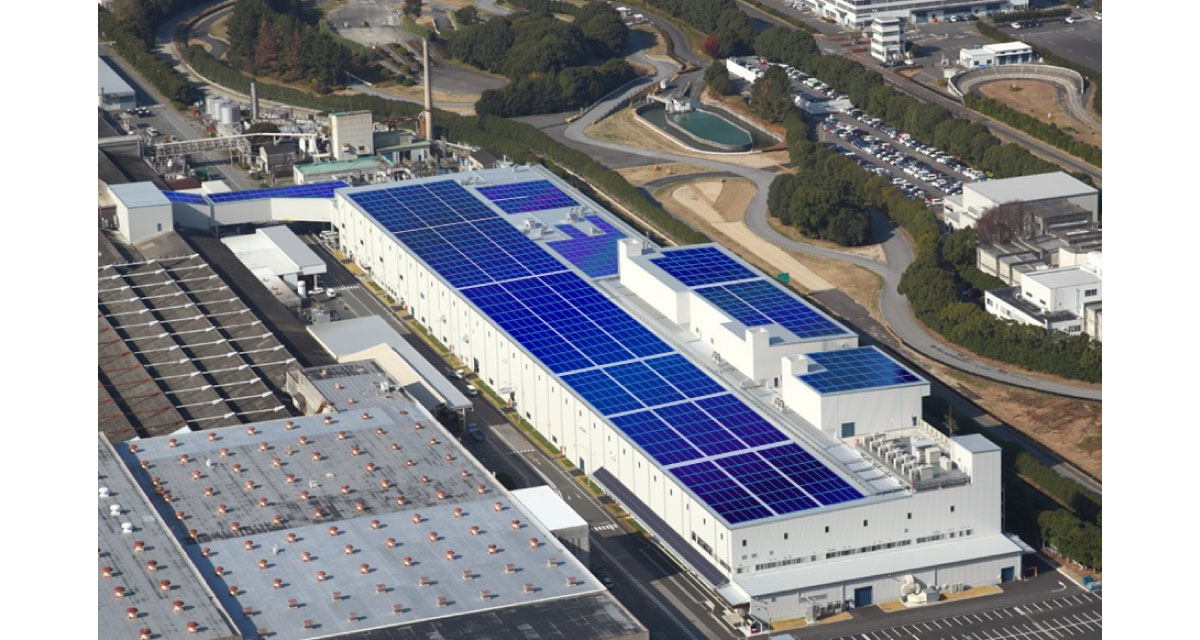
Installation of a utility-scale rooftop photovoltaic system and battery energy storage system reusing EV batteries at Okazaki Plant in Japan
MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORPORATION
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.



-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)