Promotion toward lower carbon emissions by multi-solution approach
Mazda Motor Corporation
Outline
Mazda develops multiple solutions that enable customers to offer appropriate powertrains in consideration of each region’s energy situation and power generation mix.
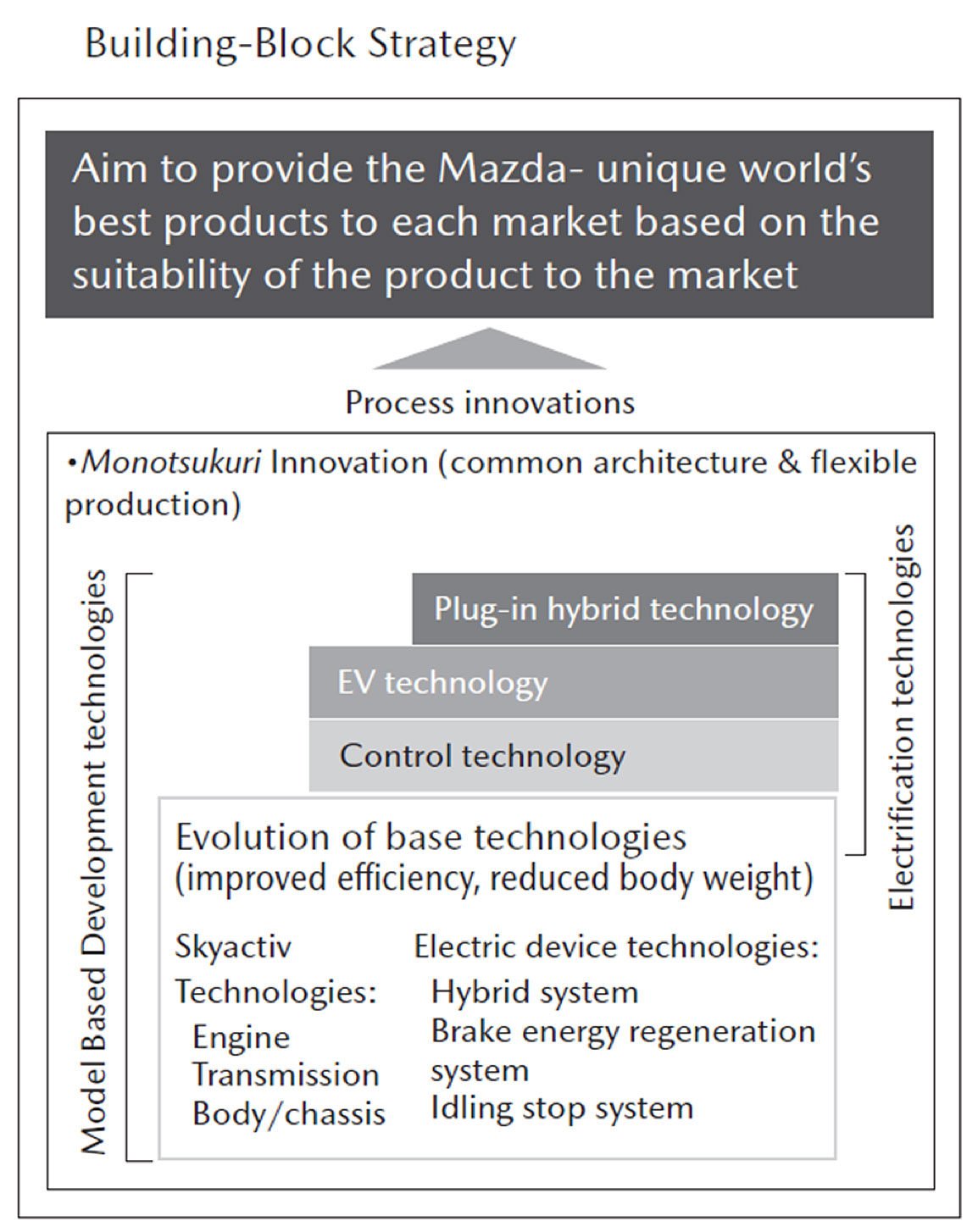
In order to realize this, Mazda promotes the Building Block Strategy for the commercial introduction of electric, plug-in and other electrified vehicles with continuing efforts to perfect the technology of internal combustion engines.
Description
[Target]
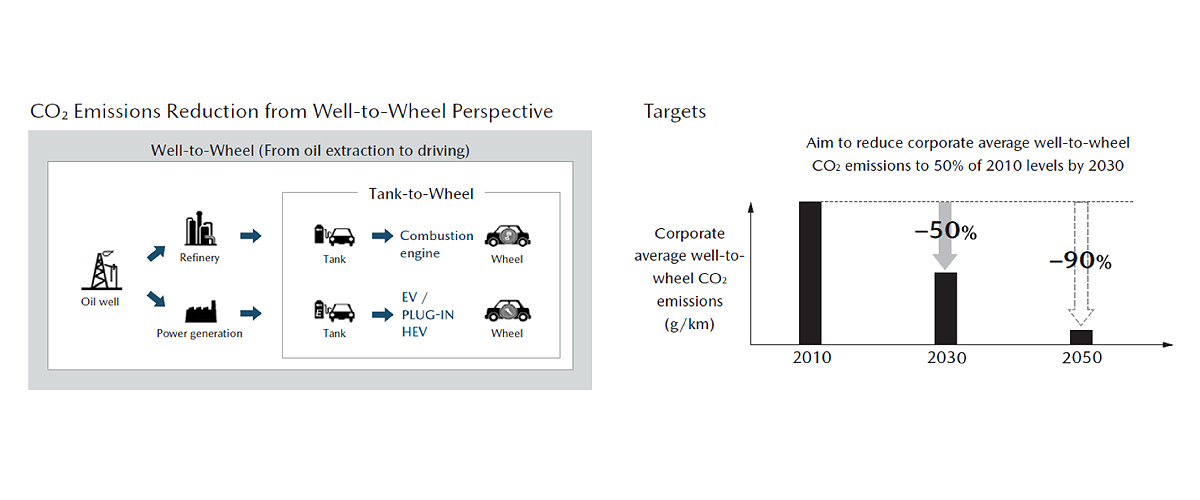
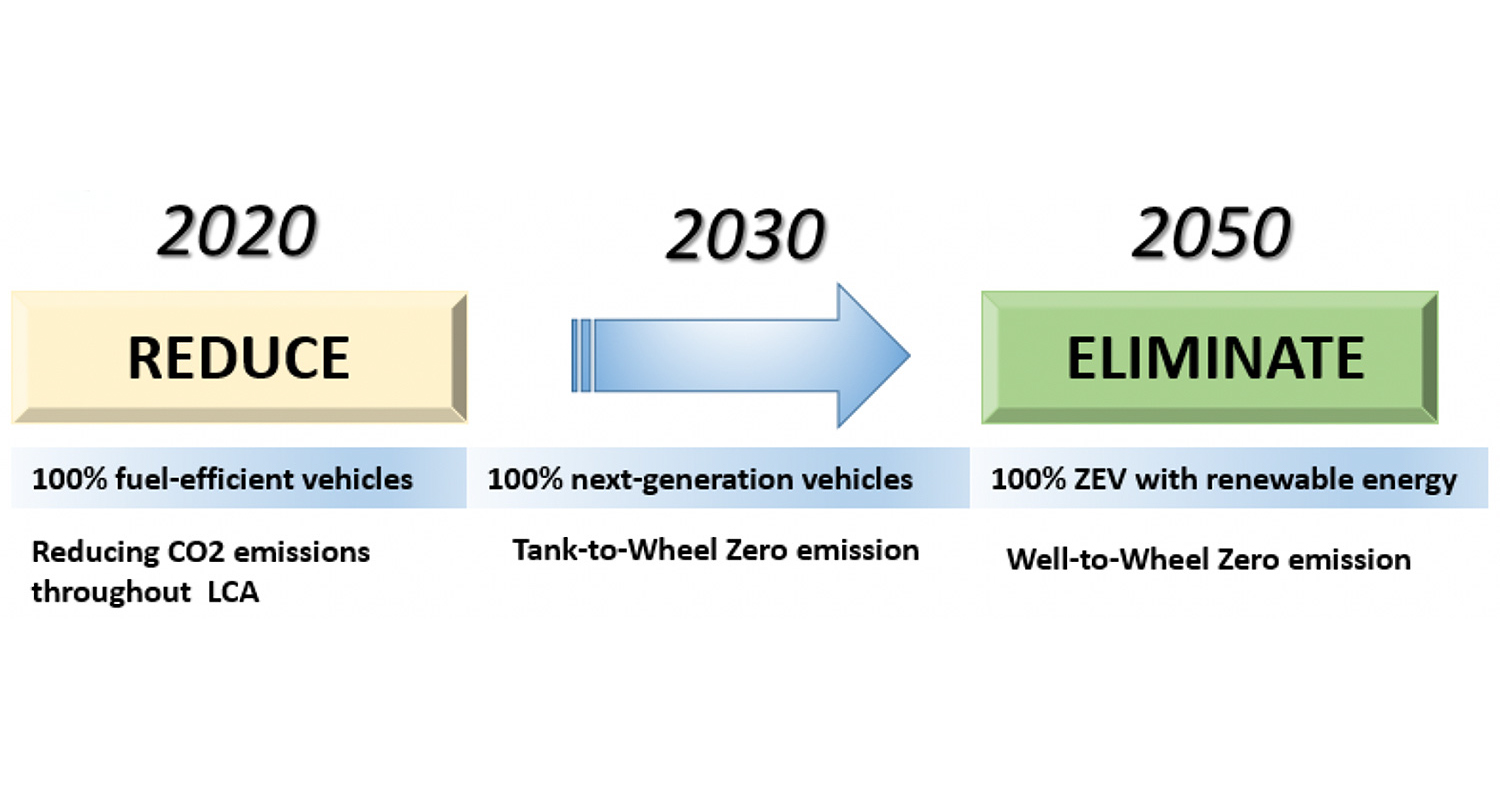
Mazda reduces corporate average well-to-wheel CO2 emissions to 50% of 2010 levels by 2030 with a view to achieving a 90% cut by 2050.
[Issues to be solved]
A) Evolution of base technologies as essential vehicle performance;
Based on the forecast that the internal combustion engine will remain a principle propulsion technology in vehicles worldwide for many years to come, Mazda thinks it is important to continue efforts to perfect the technology for CO2 reduction. Mazda thinks that internal combustion engine has room to further improve energy efficiency and it is necessary to promote the technological innovations that bring the control factors as close as possible to the ideal condition. It is also necessary to evolve the various bases technologies such as transmission efficiency, vehicle body weight reduction and aerodynamics, as well as power source.
B) Develop electrified vehicles technologies enable to meet different regional characteristics;
Mazda believes that our electric driving technology for EVs is the optimal solution for a region with sufficient clean energy resources or a region with air pollution control norms. The issue is to develop the optimal technologies for the reduction of environmental impact from LCA perspective.
C) Spread of next-generation automotive liquid fuel;
Mazda believes that liquid fuel will be an efficient and useful energy source for movable bodies equipped with internal combustion engines even in the future. In order to reduce Well-to-Wheel CO2 emissions, it is necessary to spread algae biofuel and other next-generation renewable liquid fuels.
[Specific actions]
A) Evolution of base technologies as essential vehicle performance;
Mazda has already introduced the following three internal combustion engines including ”SKYACTIV-G” as the gasoline engine, “SKYACTIV-D” as the diesel engine and ”SKYACTIV-X” as the fusion of both merits gasoline engine and diesel engine. Mazda promotes further research and development of the control factors affecting thermal efficiency, and evolves fuel economy efficiency for these engines. In addition, as well as power source, Mazda actively expands to adopt ultra-high tensile steel and aluminum, as the example of vehicle body weight reduction.
B) Development of electrified vehicles technologies enable to meet different regional characteristics;
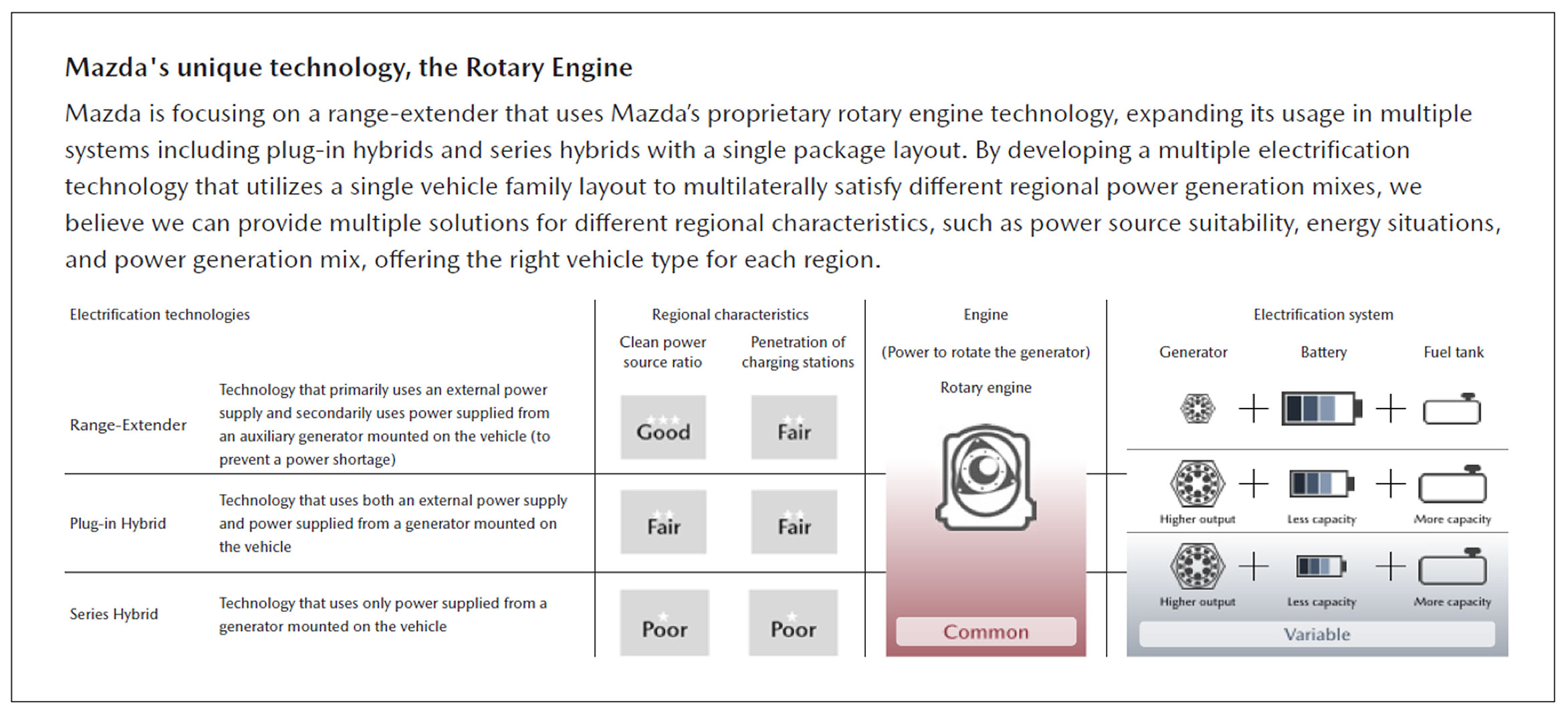
Mazda develops battery EV with a newly developed range extender powered by Mazda’s small, lightweight, and exceptionally quiet rotary engine. This range extender will recharge the battery when it is low to effectively increase the vehicle’s driving range. Also, different combinations of generators, batteries, and fuel tanks will make it possible to offer a shared packaging layout for plug-in hybrids and series hybrids.
These technological approaches enable to offer the appropriate specifications which realizes to reduce environmental impact from LCA perspective to meet with different regional characteristics.
C) Spread of next-generation automotive liquid fuel;
Mazda actively promotes collaborative efforts with other companies and between industry, academia, and government to encourage the spread of renewable liquid fuels such as microalgae biofuels. For instance, Mazda researches to create renewable bio-liquid fuel from micro algae with Hiroshima University, and also conducts various researches on Made-in-Japan Biofuels Project in collaboration with Euglena’s to spread carbon-neutral next-generation biofuels.
[Quantitative effect by this challenge]
Mazda reduces corporate average well-to-wheel CO2 emissions to 50% of 2010 levels by 2030 with a view to achieving a 90% cut by 2050.
Supplementary information
Mazda Sustainability Report 2019 (In-depth version)
https://www.mazda.com/globalassets/en/assets/csr/download/2019/2019_all.pdf
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieve 2050 decarbonization target with Net Zero Energy House!
Sekisui House, Ltd.
Achieving net-zero emissions by promoting renewable energy use through both our monozukuri and products.
DAIWA HOUSE INDUSTRY CO., LTD.