Carbon Recycling Methanol Business
MITSUBISHI GAS CHEMICAL COMPANY,INC.
Outline
Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Company Inc. (MGC) is participating with its partners in research on the effective use of CO2 for synthesis of methanol or other basic substances at the Tomakomai CO2 storage site, which is supported/sponsored by The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). Facilities being used in CO2 capture and storage (CCS) demonstration trial at a refinery in Tomakomai City, Hokkaido will be utilized for producing methanol from the captured CO2, known as CO2 capture and utilization (CCU). Research will be conducted on CCU technologies in two fiscal years until February 2021. The project will be used to identify issues concerning the economic and business feasibility of producing methanol through carbon recycling and will lead to development of carbon recycling methanol business in the future.
Description
NEDO made the call for participation for the purposes of evaluating the fundamental design of the plant, the performance of the constituent equipment, examining the economic feasibility, and surveying peripheral technologies with respect to existing CCS facilities that separate and capture CO2 from the emissions of a refinery for underground storage and carbon recycling technologies in order to effectively use CO2 for synthesis of methanol and other materials at a CO2 storage site.
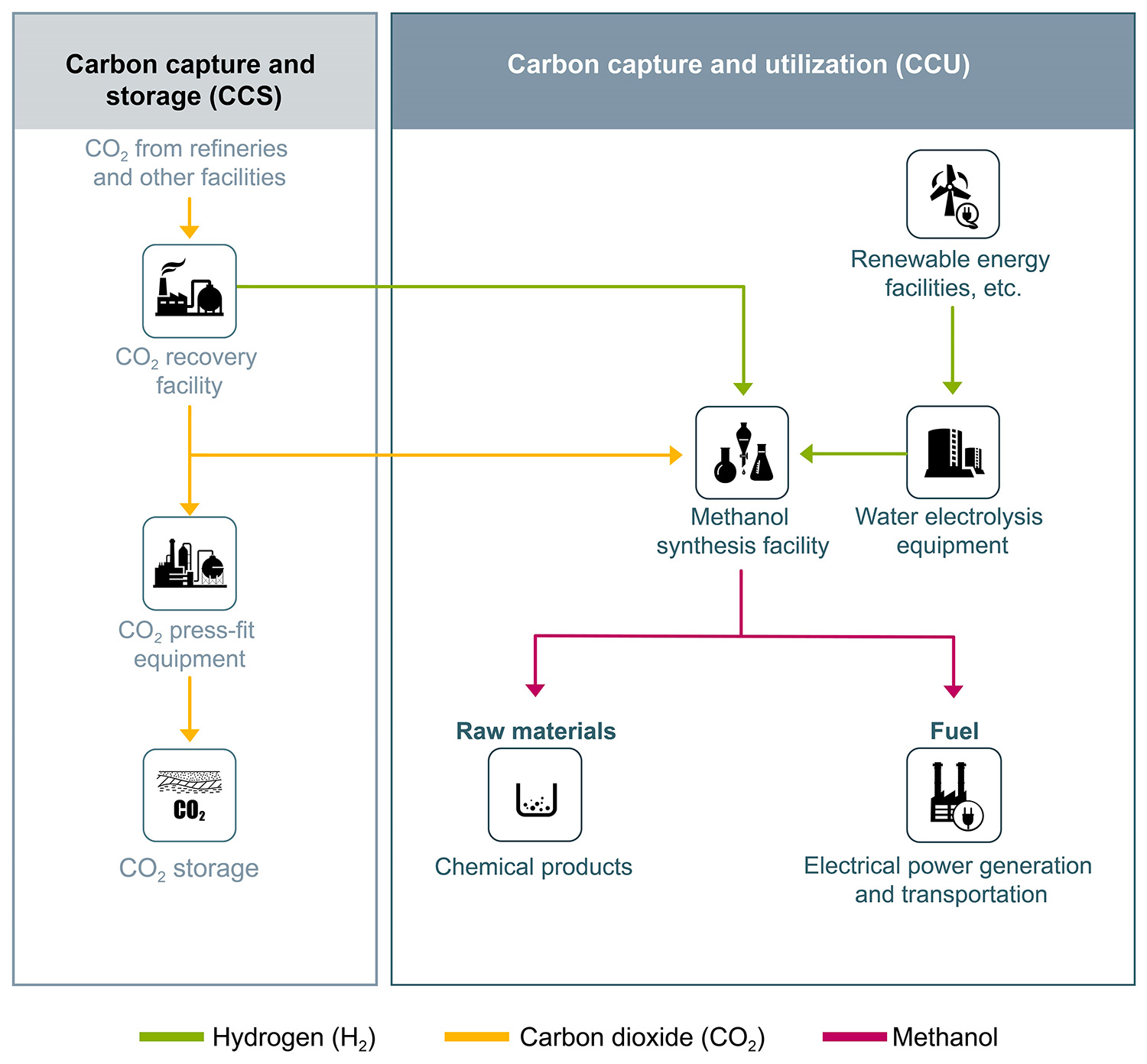
MGC and its partners have proposed producing methanol through the use of recycled carbon by making use of CO2 from CO2 recovery facilities and hydrogen produced as a by-product from a refinery or hydrogen from water electrolysis. The methanol will be used as a raw material for chemical products or as fuel. The proposal contemplates combining a carbon recycling methanol synthesis plant with a daily capacity of 20 tons with CCS facilities. The CO2 will be suitably allocated to CCS and CCU for efficient operation of the facilities.
The roadmap for carbon recycling technologies announced by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry positions methanol as a basic substance, and as a key raw material, methanol is expected to be developed for chemical product and energy applications including fuel. Demand for methanol is rising every year, with global demand reaching approximately 80 million tons in 2019, of which Japan accounted for 1.8 million tons. Domestic production of methanol, however, was terminated in the 1990s, meaning that 100% of demand relies on imports. If methanol can be produced from CO2 in Japan, this will lead to a direct decrease in CO2 and can be expected to have secondary effects such as reducing CO2 emissions from long-distance transportation.
Methanol is manufactured from natural gas and coal via synthesis gas that contains CO, CO2 and Hydrogen. During manufacture, it is necessary to activate the chemical reaction using a catalyst.
MGC’s methanol business started in the 1950s with the first successful synthesis of methanol from natural gas in Japan. Methanol production has continued with the establishment of overseas joint ventures in the 1980s and the development of original technologies and catalysts.
The stable and low-cost supply of methanol requires durable, high-performance catalysts both chemically and physically. Using catalyst development experience and expertise accumulated over many years to stably manufacture high-performance, proprietary catalysts is one of MGC’s strengths.
Through this project, MGC and its partners will identify and organize issues relating to the business of producing methanol from CO2 and make preparations for commercialization while cooperating on innovations that will lead to the creation of a low-carbon society.
Partner(s)
Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Engineering, Ltd.